Chronic Endotoxemia in Subjects with Type-1 Diabetes Is Seen Much before the Onset of Microvascular Complications
- PMID: 26367738
- PMCID: PMC4569180
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137618
Chronic Endotoxemia in Subjects with Type-1 Diabetes Is Seen Much before the Onset of Microvascular Complications
Abstract
Background: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/Endotoxin is hypothesized to play an important role in chronic inflammation associated with Type-1 diabetes (T1DM) and its complications. Endotoxin core antibodies (EndoCAb), LPS binding protein (LBP) and soluble CD14 (sCD14) act as modulators of LPS induced activation of innate immune system in vivo. For the present study we estimated the levels of LPS and its translocation markers in T1DM subjects with and without microvascular complications (MVC) and correlate them with clinical parameters of T1DM and serum inflammatory cytokine levels (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and GM-CSF).
Methods: A total of 197 subjects (64 normal glucose tolerance (NGT) subjects, 97 T1DM subjects without MVC and 36 with MVC) were included in this study and the levels of serum LPS, its translocation markers and cytokines measured by immunoassays.
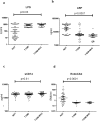
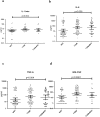
Results: Compared to NGT, T1DM subjects (both with and without MVC) had significantly higher levels of LPS, reduced levels of LBP and EndoCAb along with significant increase in the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and GM-CSF (p<0.05). No significant change was seen in the levels of these biomarkers between T1DM subjects with and without MVC.
Conclusions: Decreased levels of EndoCAb and LBP suggest sustained endotoxin activity in T1DM subjects even before the onset of microvascular complications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Notkins AL. Immunologic and genetic factors in type 1 diabetes. J Biol Chem 2002;277: 43545–8. - PubMed
-
- Peng H, Hagopian W. Environmental factors in the development of Type 1 diabetes. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2006;7: 149–62. - PubMed
-
- Nistico L, Iafusco D, Galderisi A, Fagnani C, Cotichini R, Toccaceli V, et al. Emerging effects of early environmental factors over genetic background for type 1 diabetes susceptibility: evidence from a Nationwide Italian Twin Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97: E1483–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

