Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture
- PMID: 26367794
- PMCID: PMC4755714
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14878
Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture
Abstract
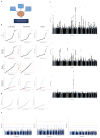
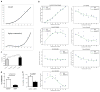
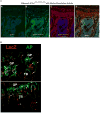
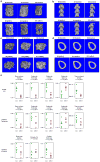
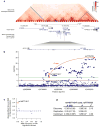
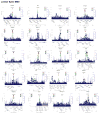
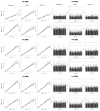
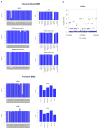
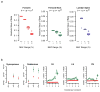
The extent to which low-frequency (minor allele frequency (MAF) between 1-5%) and rare (MAF ≤ 1%) variants contribute to complex traits and disease in the general population is mainly unknown. Bone mineral density (BMD) is highly heritable, a major predictor of osteoporotic fractures, and has been previously associated with common genetic variants, as well as rare, population-specific, coding variants. Here we identify novel non-coding genetic variants with large effects on BMD (ntotal = 53,236) and fracture (ntotal = 508,253) in individuals of European ancestry from the general population. Associations for BMD were derived from whole-genome sequencing (n = 2,882 from UK10K (ref. 10); a population-based genome sequencing consortium), whole-exome sequencing (n = 3,549), deep imputation of genotyped samples using a combined UK10K/1000 Genomes reference panel (n = 26,534), and de novo replication genotyping (n = 20,271). We identified a low-frequency non-coding variant near a novel locus, EN1, with an effect size fourfold larger than the mean of previously reported common variants for lumbar spine BMD (rs11692564(T), MAF = 1.6%, replication effect size = +0.20 s.d., Pmeta = 2 × 10(-14)), which was also associated with a decreased risk of fracture (odds ratio = 0.85; P = 2 × 10(-11); ncases = 98,742 and ncontrols = 409,511). Using an En1(cre/flox) mouse model, we observed that conditional loss of En1 results in low bone mass, probably as a consequence of high bone turnover. We also identified a novel low-frequency non-coding variant with large effects on BMD near WNT16 (rs148771817(T), MAF = 1.2%, replication effect size = +0.41 s.d., Pmeta = 1 × 10(-11)). In general, there was an excess of association signals arising from deleterious coding and conserved non-coding variants. These findings provide evidence that low-frequency non-coding variants have large effects on BMD and fracture, thereby providing rationale for whole-genome sequencing and improved imputation reference panels to study the genetic architecture of complex traits and disease in the general population.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR065530/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AR061430/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 20000/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AR045654/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K01 AR062655/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042143/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG027576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045614/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 102215/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG005407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AR045583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042140/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045647/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AR058973/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020069/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035582/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR057235/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005394/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063702/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 119462-1/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U01 AR045580/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG018197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR066160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045632/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

