Standing your ground to exoribonucleases: Function of Flavivirus long non-coding RNAs
- PMID: 26368052
- PMCID: PMC4744573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.09.009
Standing your ground to exoribonucleases: Function of Flavivirus long non-coding RNAs
Abstract
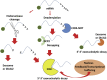
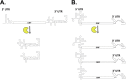
Members of the Flaviviridae (e.g., Dengue virus, West Nile virus, and Hepatitis C virus) contain a positive-sense RNA genome that encodes a large polyprotein. It is now also clear most if not all of these viruses also produce an abundant subgenomic long non-coding RNA. These non-coding RNAs, which are called subgenomic flavivirus RNAs (sfRNAs) or Xrn1-resistant RNAs (xrRNAs), are stable decay intermediates generated from the viral genomic RNA through the stalling of the cellular exoribonuclease Xrn1 at highly structured regions. Several functions of these flavivirus long non-coding RNAs have been revealed in recent years. The generation of these sfRNAs/xrRNAs from viral transcripts results in the repression of Xrn1 and the dysregulation of cellular mRNA stability. The abundant sfRNAs also serve directly as a decoy for important cellular protein regulators of the interferon and RNA interference antiviral pathways. Thus the generation of long non-coding RNAs from flaviviruses, hepaciviruses and pestiviruses likely disrupts aspects of innate immunity and may directly contribute to viral replication, cytopathology and pathogenesis.
Keywords: Exoribonuclease; Flavivirus; IRES; Long non-coding RNA; RNA decay; RNA stability; Untranslated regions.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bashkirov V.I., Solinger J.A., Heyer W.D. Identification of functional domains in the Sep1 protein (=Kem1, Xrn1), which is required for transition through meiotic prophase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chromosoma. 1995;104(November (3)):215–222. - PubMed
-
- Bassett A.R., Akhtar A., Barlow D.P., Bird A.P., Brockdorff N., Duboule D., Ephrussi A., Ferguson-Smith A.C., Gingeras T.R., Haerty W., Higgs D.R., Miska E.A., Ponting C.P. Considerations when investigating lncRNA function in vivo. Elife. 2014;14(August (3)):e03058. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bell C.L., Yu D., Smolke C.D., Geall A.J., Beard C.W., Mason P.W. Control of alphavirus-based gene expression using engineered riboswitches. Virology. 2015;483(May):302–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

