Perhexiline activates KLF14 and reduces atherosclerosis by modulating ApoA-I production
- PMID: 26368306
- PMCID: PMC4607137
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI79048
Perhexiline activates KLF14 and reduces atherosclerosis by modulating ApoA-I production
Abstract
Recent genome-wide association studies have revealed that variations near the gene locus encoding the transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 14 (KLF14) are strongly associated with HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) levels, metabolic syndrome, and coronary heart disease. However, the precise mechanisms by which KLF14 regulates lipid metabolism and affects atherosclerosis remain largely unexplored. Here, we report that KLF14 is dysregulated in the liver of 2 dyslipidemia mouse models. We evaluated the effects of both KLF14 overexpression and genetic inactivation and determined that KLF14 regulates plasma HDL-C levels and cholesterol efflux capacity by modulating hepatic ApoA-I production. Hepatic-specific Klf14 deletion in mice resulted in decreased circulating HDL-C levels. In an attempt to pharmacologically target KLF14 as an experimental therapeutic approach, we identified perhexiline, an approved therapeutic small molecule presently in clinical use to treat angina and heart failure, as a KLF14 activator. Indeed, in WT mice, treatment with perhexiline increased HDL-C levels and cholesterol efflux capacity via KLF14-mediated upregulation of ApoA-I expression. Moreover, perhexiline administration reduced atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Together, these results provide comprehensive insight into the KLF14-dependent regulation of HDL-C and subsequent atherosclerosis and indicate that interventions that target the KLF14 pathway should be further explored for the treatment of atherosclerosis.
Figures
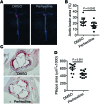

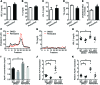
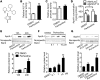

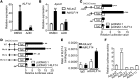

Similar articles
-
Germline deletion of Krüppel-like factor 14 does not increase risk of diet induced metabolic syndrome in male C57BL/6 mice.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Dec;1863(12):3277-3285. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.09.021. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28962896 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor 14 deletion in myeloid cells accelerates atherosclerotic lesion development.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Jan 29;118(2):475-488. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab027. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33538785 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 prevents atherosclerosis by suppression of hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 and induction of adiponectin in mice.Circulation. 2015 May 26;131(21):1861-71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.015308. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25794851 Free PMC article.
-
Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review.
-
The role of Krüppel-like factor 14 in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Aug;263:352-360. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.06.011. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28641818 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of transcription factors in the pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting of vascular diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Apr 30;11:1384294. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1384294. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38745757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germline deletion of Krüppel-like factor 14 does not increase risk of diet induced metabolic syndrome in male C57BL/6 mice.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Dec;1863(12):3277-3285. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.09.021. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28962896 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Transformative Platforms for the Discovery of Causative Genes in Cardiovascular Diseases.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021 Jun;35(3):637-654. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07175-1. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021. PMID: 33856594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergetic Effect of rHDL and LXR Agonist on Reduction of Atherosclerosis in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 16;11:513031. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.513031. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33390931 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of Endothelial Dysfunction of Berberine in Atherosclerotic Mice and Mechanism Exploring through TMT-Based Proteomics.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 May 31;2020:8683404. doi: 10.1155/2020/8683404. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32566106 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 DK052913/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA178627/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088391/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052913/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068878/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK089503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK097153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA178627/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068878/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL088391/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL105114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK52913/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK097153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK89503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

