BMI Affects the Relationship between Long Chain N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake and Stroke Risk: a Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26369699
- PMCID: PMC4572932
- DOI: 10.1038/srep14161
BMI Affects the Relationship between Long Chain N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake and Stroke Risk: a Meta-Analysis
Abstract
We performed a meta-analysis to clarify the relationship between long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) intake and stroke risk. Relevant studies were identified by searching online databases through May 2015. Log relative risks (RRs) of the highest versus the lowest for cohort studies were weighed by the inverse variance method to obtain pooled RRs. Fourteen prospective cohort studies including 514,483 individuals and 9,065 strokes were included. The pooled RR of overall stroke risk for long chain n-3 PUFA intake was 0.87 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.79-0.95]. Stratification analysis showed that higher long chain n-3 PUFAs intake was associated with reduced fatal stroke risk (RR = 0.84; 95% CI, 0.73-0.97), reduced stroke risk for BMI < 24 (RR = 0.86; 95% CI, 0.75-0.98) and reduced stroke risk for females (RR = 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.92), but was not associated with stroke risk for either BMI ≥ 24 or men. This meta-analysis reveals that higher long chain n-3 PUFA intake is inversely associated with risk of stroke morbidity and mortality with BMI and sex as key factors influencing this risk. Individuals should be encouraged to manage their body weight while increasing their intake of long chain n-3 PUFAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
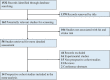
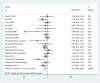

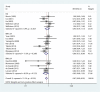


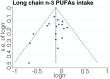
References
-
- Prencipe M. et al. Stroke, Disability, and Dementia Results of a Population Survey. Stroke 28, 531–536 (1997). - PubMed
-
- He K. Fish. long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and prevention of cardiovascular disease—eat fish or take fish oil supplement? Prog Cardiovasc Dis 52, 95–114 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D. & Wu J. H. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease Effects on Risk Factors, Molecular Pathways, and Clinical Events. J Am Coll Cardiol 58, 2047–2067 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Thies F. et al. Association of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with stability of atherosclerotic plaques: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 361, 477–485 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

