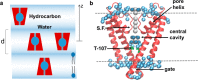
Pore hydration states of KcsA potassium channels in membranes
- PMID: 26370089
- PMCID: PMC4646329
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.661819
Pore hydration states of KcsA potassium channels in membranes
Abstract
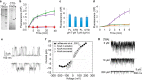
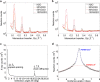
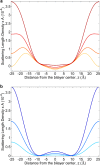
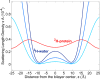
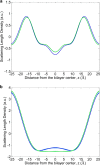
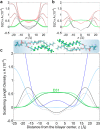
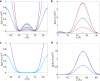
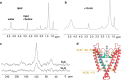
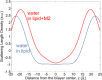
Water-filled hydrophobic cavities in channel proteins serve as gateways for transfer of ions across membranes, but their properties are largely unknown. We determined water distributions along the conduction pores in two tetrameric channels embedded in lipid bilayers using neutron diffraction: potassium channel KcsA and the transmembrane domain of M2 protein of influenza A virus. For the KcsA channel in the closed state, the distribution of water is peaked in the middle of the membrane, showing water in the central cavity adjacent to the selectivity filter. This water is displaced by the channel blocker tetrabutyl-ammonium. The amount of water associated with the channel was quantified, using neutron diffraction and solid state NMR. In contrast, the M2 proton channel shows a V-shaped water profile across the membrane, with a narrow constriction at the center, like the hourglass shape of its internal surface. These two types of water distribution are therefore very different in their connectivity to the bulk water. The water and protein profiles determined here provide important evidence concerning conformation and hydration of channels in membranes and the potential role of pore hydration in channel gating.
Keywords: KcsA; M2; influenza virus; ion channels; lipid bilayer; neutron diffraction; nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); potassium channel.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Hilser V. J. (2011) Structural biology: finding the wet spots. Nature 469, 166–167 - PubMed
-
- Ball P. (2008) Water as an active constituent in cell biology. Chem. Rev. 108, 74–108 - PubMed
-
- Doyle D. A., Morais Cabral J., Pfuetzner R. A., Kuo A., Gulbis J. M., Cohen S. L., Chait B. T., and MacKinnon R. (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 280, 69–77 - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y., Morais-Cabral J. H., Kaufman A., and MacKinnon R. (2001) Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel-Fab complex at 2.0 angstrom resolution. Nature 414, 43–48 - PubMed
-
- Yu F. H., Yarov-Yarovoy V., Gutman G. A., and Catterall W. A. (2005) Overview of molecular relationships in the voltage-gated ion channel superfamily. Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 387–395 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

