A Phospholipid-Protein Complex from Antarctic Krill Reduced Plasma Homocysteine Levels and Increased Plasma Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) and Carnitine Levels in Male Wistar Rats
- PMID: 26371012
- PMCID: PMC4584349
- DOI: 10.3390/md13095706
A Phospholipid-Protein Complex from Antarctic Krill Reduced Plasma Homocysteine Levels and Increased Plasma Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) and Carnitine Levels in Male Wistar Rats
Abstract
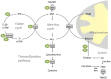
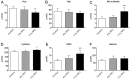
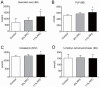
Seafood is assumed to be beneficial for cardiovascular health, mainly based on plasma lipid lowering and anti-inflammatory effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. However, other plasma risk factors linked to cardiovascular disease are less studied. This study aimed to penetrate the effect of a phospholipid-protein complex (PPC) from Antarctic krill on one-carbon metabolism and production of trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) in rats. Male Wistar rats were fed isoenergetic control, 6%, or 11% PPC diets for four weeks. Rats fed PPC had reduced total homocysteine plasma level and increased levels of choline, dimethylglycine and cysteine, whereas the plasma level of methionine was unchanged compared to control. PPC feeding increased the plasma level of TMAO, carnitine, its precursors trimethyllysine and γ-butyrobetaine. There was a close correlation between plasma TMAO and carnitine, trimethyllysine, and γ-butyrobetaine, but not between TMAO and choline. The present data suggest that PPC has a homocysteine lowering effect and is associated with altered plasma concentrations of metabolites related to one-carbon metabolism and B-vitamin status in rats. Moreover, the present study reveals a non-obligatory role of gut microbiota in the increased plasma TMAO level as it can be explained by the PPC's content of TMAO. The increased level of carnitine and carnitine precursors is interpreted to reflect increased carnitine biosynthesis.
Keywords: Euphausia superba; Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; carnitine; homocysteine; one-carbon metabolism; phospholipid-protein complex; trimethylamine-N-oxide.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Krill oil reduces plasma triacylglycerol level and improves related lipoprotein particle concentration, fatty acid composition and redox status in healthy young adults - a pilot study.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Dec 15;14:163. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0162-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26666303 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Phospholipid-Protein Complex from Krill with Antioxidative and Immunomodulating Properties Reduced Plasma Triacylglycerol and Hepatic Lipogenesis in Rats.Mar Drugs. 2015 Jul 16;13(7):4375-97. doi: 10.3390/md13074375. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26193284 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of intestinal microbiota-dependent production of pro-atherogenic trimethylamine N-oxide by shifting L-carnitine microbial degradation.Life Sci. 2014 Nov 11;117(2):84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.09.028. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25301199
-
Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO), Diet and Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021 Feb 17;23(4):12. doi: 10.1007/s11883-021-00910-x. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021. PMID: 33594574 Review.
-
TMAO: A small molecule of great expectations.Nutrition. 2015 Nov-Dec;31(11-12):1317-23. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.05.006. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 26283574 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary volatile metabolites of amygdala-kindled mice reveal novel biomarkers associated with temporal lobe epilepsy.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 22;9(1):10586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46373-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31332211 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between serum trimethylamine N-oxide and exposure to dioxin-like pollutants.Environ Res. 2018 Apr;162:211-218. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Environ Res. 2018. PMID: 29353125 Free PMC article.
-
Krill oil reduces plasma triacylglycerol level and improves related lipoprotein particle concentration, fatty acid composition and redox status in healthy young adults - a pilot study.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Dec 15;14:163. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0162-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26666303 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary factors, gut microbiota, and serum trimethylamine-N-oxide associated with cardiovascular disease in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos.Am J Clin Nutr. 2021 Jun 1;113(6):1503-1514. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab001. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33709132 Free PMC article.
-
Dysbiotic 1-carbon metabolism in cardiac muscle remodeling.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Mar;235(3):2590-2598. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29163. Epub 2019 Sep 5. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31489638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wergedahl H., Gudbrandsen O.A., Rost T.H., Berge R.K. Combination of fish oil and fish protein hydrolysate reduces the plasma cholesterol level with a concurrent increase in hepatic cholesterol level in high-fat-fed Wistar rats. Nutrition. 2009;25:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2008.07.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bjorndal B., Vik R., Brattelid T., Vigerust N.F., Burri L., Bohov P., Nygard O., Skorve J., Berge R.K. Krill powder increases liver lipid catabolism and reduces glucose mobilization in tumor necrosis factor-alpha transgenic mice fed a high-fat diet. Metabolism. 2012;61:1461–1472. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2012.03.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

