Maternal vaccination with a fimbrial tip adhesin and passive protection of neonatal mice against lethal human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge
- PMID: 26371126
- PMCID: PMC4645407
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00858-15
Maternal vaccination with a fimbrial tip adhesin and passive protection of neonatal mice against lethal human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge
Abstract
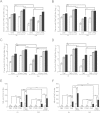
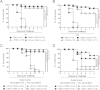
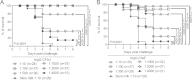
Globally, enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is a leading cause of childhood and travelers' diarrhea, for which an effective vaccine is needed. Prevalent intestinal colonization factors (CFs) such as CFA/I fimbriae and heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) are important virulence factors and protective antigens. We tested the hypothesis that donor strand-complemented CfaE (dscCfaE), a stabilized form of the CFA/I fimbrial tip adhesin, is a protective antigen, using a lethal neonatal mouse ETEC challenge model and passive dam vaccination. For CFA/I-ETEC strain H10407, which has been extensively studied in volunteers, an inoculum of 2 × 10(7) bacteria resulted in 50% lethal doses (LD50) in neonatal DBA/2 mice. Vaccination of female DBA/2 mice with CFA/I fimbriae or dscCfaE, each given with a genetically attenuated LT adjuvant (LTK63) by intranasal or orogastric delivery, induced high antigen-specific serum IgG and fecal IgA titers and detectable milk IgA responses. Neonates born to and suckled by dams antenatally vaccinated with each of these four regimens showed 78 to 93% survival after a 20× LD50 challenge with H10407, compared to 100% mortality in pups from dams vaccinated with sham vaccine or LTK63 only. Crossover experiments showed that high pup survival rates after ETEC challenge were associated with suckling but not birthing from vaccinated dams, suggesting that vaccine-specific milk antibodies are protective. In corroboration, preincubation of the ETEC inoculum with antiadhesin and antifimbrial bovine colostral antibodies conferred a dose-dependent increase in pup survival after challenge. These findings indicate that the dscCfaE fimbrial tip adhesin serves as a protective passive vaccine antigen in this small animal model and merits further evaluation.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity of a prototype enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli adhesin vaccine in mice and nonhuman primates.Vaccine. 2016 Jan 4;34(2):284-291. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.11.017. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 26597148
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Adhesin-Toxoid Multiepitope Fusion Antigen CFA/I/II/IV-3xSTaN12S-mnLTG192G/L211A-Derived Antibodies Inhibit Adherence of Seven Adhesins, Neutralize Enterotoxicity of LT and STa Toxins, and Protect Piglets against Diarrhea.Infect Immun. 2018 Feb 20;86(3):e00550-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00550-17. Print 2018 Mar. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29263112 Free PMC article.
-
Prime-boost vaccine regimen confers protective immunity to human-derived enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Vaccine. 2005 Mar 31;23(19):2430-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.11.026. Vaccine. 2005. PMID: 15752829
-
Strategies to overexpress enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) colonization factors for the construction of oral whole-cell inactivated ETEC vaccine candidates.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Mar;93(6):2291-300. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-3930-6. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22350259 Review.
-
Current Progress in Developing Subunit Vaccines against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Associated Diarrhea.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Sep;22(9):983-91. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00224-15. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26135975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibodies derived from an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) adhesin tip MEFA (multiepitope fusion antigen) against adherence of nine ETEC adhesins: CFA/I, CS1, CS2, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6, CS21 and EtpA.Vaccine. 2016 Jun 30;34(31):3620-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 May 24. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27228947 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of avian antibodies as prophylaxis against enterotoxigenic escherichia coli colonization.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 19;13:1011200. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1011200. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341430 Free PMC article.
-
São Paulo School of Advanced Sciences on Vaccines: an overview.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020 Apr 6;26:e20190061. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2019-0061. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32362926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment and Validation of Pathogenic CS17+ and CS19+ Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Challenge Models in the New World Primate Aotus nancymaae.Infect Immun. 2021 Feb 16;89(3):e00479-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00479-20. Print 2021 Feb 16. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 33288648 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy Evaluation of an Intradermally Delivered Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CF Antigen I Fimbrial Tip Adhesin Vaccine Coadministered with Heat-Labile Enterotoxin with LT(R192G) against Experimental Challenge with Enterotoxigenic E. coli H10407 in Healthy Adult Volunteers.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 29;12(2):288. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020288. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker-Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, Burney P, Carapetis J, Chen H, Chou D, et al. . 2012. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380:2095–2128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, Wu Y, Sow SO, Sur D, Breiman RF, Faruque AS, Zaidi AK, Saha D, Alonso PL, Tamboura B, Sanogo D, Onwuchekwa U, Manna B, Ramamurthy T, Kanungo S, Ochieng JB, Omore R, Oundo JO, Hossain A, Das SK, Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Quadri F, Adegbola RA, Antonio M, Hossain MJ, Akinsola A, Mandomando I, Nhampossa T, Acacio S, Biswas K, O'Reilly CE, Mintz ED, Berkeley LY, Muhsen K, Sommerfelt H, Robins-Browne RM, Levine MM. 2013. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet 382:209–222. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gaastra W, Sommerfelt H, van Dijk L, Kusters JG, Svennerholm AM, Grewal HM. 2002. Antigenic variation within the subunit protein of members of the colonization factor antigen I group of fimbrial proteins in human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Int J Med Microbiol 292:43–50. doi:10.1078/1438-4221-00189. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

