EBS7 is a plant-specific component of a highly conserved endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation system in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 26371323
- PMCID: PMC4593087
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1511724112
EBS7 is a plant-specific component of a highly conserved endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation system in Arabidopsis
Abstract
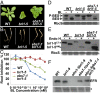
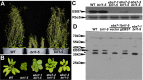
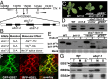
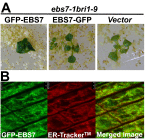
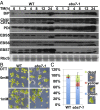
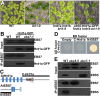
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (ERAD) is an essential part of an ER-localized protein quality-control system for eliminating terminally misfolded proteins. Recent studies have demonstrated that the ERAD machinery is conserved among yeast, animals, and plants; however, it remains unknown if the plant ERAD system involves plant-specific components. Here we report that the Arabidopsis ethyl methanesulfonate-mutagenized brassinosteroid-insensitive 1 suppressor 7 (EBS7) gene encodes an ER membrane-localized ERAD component that is highly conserved in land plants. Loss-of-function ebs7 mutations prevent ERAD of brassinosteroid insensitive 1-9 (bri1-9) and bri1-5, two ER-retained mutant variants of the cell-surface receptor for brassinosteroids (BRs). As a result, the two mutant receptors accumulate in the ER and consequently leak to the plasma membrane, resulting in the restoration of BR sensitivity and phenotypic suppression of the bri1-9 and bri1-5 mutants. EBS7 accumulates under ER stress, and its mutations lead to hypersensitivity to ER and salt stresses. EBS7 interacts with the ER membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase Arabidopsis thaliana HMG-CoA reductase degradation 1a (AtHrd1a), one of the central components of the Arabidopsis ERAD machinery, and an ebs7 mutation destabilizes AtHrd1a to reduce polyubiquitination of bri1-9. Taken together, our results uncover a plant-specific component of a plant ERAD pathway and also suggest its likely biochemical function.
Keywords: EMS-mutagenized bri1 suppressor; ERAD; brassinosteroid receptor BRI1; ubiquitin ligase E3; unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Denic V, Quan EM, Weissman JS. A luminal surveillance complex that selects misfolded glycoproteins for ER-associated degradation. Cell. 2006;126(2):349–359. - PubMed
-
- Gauss R, Jarosch E, Sommer T, Hirsch C. A complex of Yos9p and the HRD ligase integrates endoplasmic reticulum quality control into the degradation machinery. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(8):849–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

