Phosphodiesterase 4D acts downstream of Neuropilin to control Hedgehog signal transduction and the growth of medulloblastoma
- PMID: 26371509
- PMCID: PMC4569902
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.07068
Phosphodiesterase 4D acts downstream of Neuropilin to control Hedgehog signal transduction and the growth of medulloblastoma
Abstract
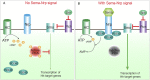
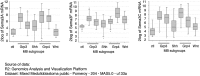
Alterations in Hedgehog (Hh) signaling lead to birth defects and cancers including medulloblastoma, the most common pediatric brain tumor. Although inhibitors targeting the membrane protein Smoothened suppress Hh signaling, acquired drug resistance and tumor relapse call for additional therapeutic targets. Here we show that phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) acts downstream of Neuropilins to control Hh transduction and medulloblastoma growth. PDE4D interacts directly with Neuropilins, positive regulators of Hh pathway. The Neuropilin ligand Semaphorin3 enhances this interaction, promoting PDE4D translocation to the plasma membrane and cAMP degradation. The consequent inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA) enhances Hh transduction. In the developing cerebellum, genetic removal of Neuropilins reduces Hh signaling activity and suppresses proliferation of granule neuron precursors. In mouse medulloblastoma allografts, PDE4D inhibitors suppress Hh transduction and inhibit tumor growth. Our findings reveal a new regulatory mechanism of Hh transduction, and highlight PDE4D as a promising target to treat Hh-related tumors.
Keywords: Hedgehog signal transduction; Neuropilin; Phosphodiesterase 4D; Semaphorin 3; developmental biology; medulloblastoma; mouse; neuroscience; stem cells; tumors resistant to Smo-inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Hedgehog Signal Transduction: Key Players, Oncogenic Drivers, and Cancer Therapy.Dev Cell. 2016 Aug 22;38(4):333-44. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.07.026. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27554855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myomegalin regulates Hedgehog pathway by controlling PDE4D at the centrosome.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Sep 1;32(19):1807-1817. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-02-0064. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34260267 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilin-2 contributes to tumorigenicity in a mouse model of Hedgehog pathway medulloblastoma.J Neurooncol. 2013 Nov;115(2):161-8. doi: 10.1007/s11060-013-1216-1. Epub 2013 Sep 12. J Neurooncol. 2013. PMID: 24026530 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilins are positive regulators of Hedgehog signal transduction.Genes Dev. 2011 Nov 15;25(22):2333-46. doi: 10.1101/gad.173054.111. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 22051878 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Feb 20;18(1):8-20. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2018.2756. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29274272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of thieno- and benzopyrimidinone inhibitors of the Hedgehog signaling pathway reveals PDE4-dependent and PDE4-independent mechanisms of action.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Apr 15;26(8):1947-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.03.013. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 26976215 Free PMC article.
-
The G protein Gαs acts as a tumor suppressor in sonic hedgehog signaling-driven tumorigenesis.Cell Cycle. 2016 May 18;15(10):1325-30. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1164371. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27052725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog Signal Transduction: Key Players, Oncogenic Drivers, and Cancer Therapy.Dev Cell. 2016 Aug 22;38(4):333-44. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.07.026. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27554855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissection of the microRNA Network Regulating Hedgehog Signaling in Drosophila.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 28;10:866491. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.866491. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573695 Free PMC article.
-
Myomegalin regulates Hedgehog pathway by controlling PDE4D at the centrosome.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Sep 1;32(19):1807-1817. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-02-0064. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34260267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appleton BA, Wu P, Maloney J, Yin J, Liang WC, Stawicki S, Mortara K, Bowman KK, Elliott JM, Desmarais W, Bazan JF, Bagri A, Tessier-Lavigne M, Koch AW, Wu Y, Watts RJ, Wiesmann C. Structural studies of neuropilin/antibody complexes provide insights into semaphorin and VEGF binding. The EMBO Journal. 2007;26:4902–4912. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601906. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

