Factors associated with abnormal spirometry among HIV-infected individuals
- PMID: 26372280
- PMCID: PMC4571285
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000750
Factors associated with abnormal spirometry among HIV-infected individuals
Abstract
Objective: HIV-infected individuals are susceptible to development of chronic lung diseases, but little is known regarding the prevalence and risk factors associated with different spirometric abnormalities in this population. We sought to determine the prevalence, risk factors and performance characteristics of risk factors for spirometric abnormalities among HIV-infected individuals.
Design: Cross-sectional cohort study.
Methods: We analyzed cross-sectional US data from the NHLBI-funded Lung-HIV consortium - a multicenter observational study of heterogeneous groups of HIV-infected participants in diverse geographic sites. Logistic regression analysis was performed to determine factors statistically significantly associated with spirometry patterns.
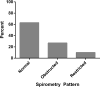
Results: A total of 908 HIV-infected individuals were included. The median age of the cohort was 50 years, 78% were men and 68% current smokers. An abnormal spirometry pattern was present in 37% of the cohort: 27% had obstructed and 10% had restricted spirometry patterns. Overall, age, smoking status and intensity, history of Pneumocystis infection, asthma diagnosis and presence of respiratory symptoms were independently associated with an abnormal spirometry pattern. Regardless of the presence of respiratory symptoms, five HIV-infected participants would need to be screened with spirometry to diagnose two individuals with any abnormal spirometry pattern.
Conclusions: Nearly 40% of a diverse US cohort of HIV-infected individuals had an abnormal spirometry pattern. Specific characteristics including age, smoking status, respiratory infection history and respiratory symptoms can identify those at risk for abnormal spirometry. The high prevalence of abnormal spirometry and the poor predictive capability of respiratory symptoms to identify abnormal spirometry should prompt clinicians to consider screening spirometry in HIV-infected populations.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no relevant conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Walensky RP, Paltiel AD, Losina E, Mercincavage LM, Schackman BR, Sax PE, et al. The survival benefits of AIDS treatment in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Braithwaite RS, Justice AC, Chang CC, Fusco JS, Raffanti SR, Wong JB, et al. Estimating the proportion of patients infected with HIV who will die of comorbid diseases. Am J Med. 2005;118:890–898. - PubMed
-
- Wood E, Hogg RS, Lima VD, Kerr T, Yip B, Marshall BD, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy and survival in HIV-infected injection drug users. JAMA. 2008;300:550–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090342/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL103192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL090313/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090313/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI118591/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090335/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL121814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036297/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-HD-32632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090483/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-37984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090316/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000722/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090331/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-34993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL090483/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL087713/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL090331/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-42590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5-MO1-RR-00722/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-31834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126549/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-37613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States