Roles of Klf5 Acetylation in the Self-Renewal and the Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- PMID: 26372456
- PMCID: PMC4570665
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138168
Roles of Klf5 Acetylation in the Self-Renewal and the Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
Abstract
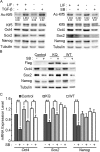
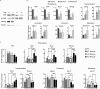
Transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 5 (Klf5) plays important roles in the formation of the inner cell mass (ICM) and the trophectoderm during embryogenesis, as well as the self-renewal and the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Acetylation of KLF5 has been shown to reverse the transcriptional activity of KLF5 in human epidermal cells and prostate cancer cells. Whether Klf5 acetylation contributes to the lineage specification in the blastocyst and pluripotency maintenance in ESCs remains unexplored. Here, we showed the ubiquitous expression of acetylated Klf5 in the ICM and the trophectoderm, ruling out the possibility that differential acetylation status of Klf5 leads to the lineage specification in the blastocyst. We found that K358Q mutation, mimicking acetylation, enhances the transcriptional activity of Klf5 for pluripotency genes in ESCs, and that K358Q Klf5 is more potent in pluripotency maintenance and in somatic cell reprogramming, compared to K358R Klf5. In ESCs, Klf5 acetylation, stimulated by TGF-β signaling, is involved in enhancing Sox2 expression. Moreover, upon ESC differentiation, acetylation of Klf5 facilitates the suppression of many differentiation genes, except for that K358Q Klf5 activates Cdx2, promoting trophectodermal differentiation. In summary, our results revealed the regulatory functions of Klf5 acetylation in ESC self-renewal and differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulatory role of Klf5 in early mouse development and in embryonic stem cells.Vitam Horm. 2011;87:381-97. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386015-6.00037-8. Vitam Horm. 2011. PMID: 22127252 Review.
-
Krüppel-like factor 5 is essential for blastocyst development and the normal self-renewal of mouse ESCs.Cell Stem Cell. 2008 Nov 6;3(5):555-67. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.09.003. Cell Stem Cell. 2008. PMID: 18983969
-
Klf5 regulates lineage formation in the pre-implantation mouse embryo.Development. 2010 Dec;137(23):3953-63. doi: 10.1242/dev.054775. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Development. 2010. PMID: 20980403 Free PMC article.
-
Klf5 is involved in self-renewal of mouse embryonic stem cells.J Cell Sci. 2008 Aug 15;121(Pt 16):2629-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.027599. Epub 2008 Jul 24. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18653541
-
Roles of TGF-β family signals in the fate determination of pluripotent stem cells.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Aug;32:98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.017. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24910449 Review.
Cited by
-
Aging and the Krüppel-like factors.Trends Cell Mol Biol. 2017;12:1-15. Trends Cell Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 29416266 Free PMC article.
-
KLF4 enhances transplantation-induced hematopoiesis by inhibiting TLRs and noncanonical NFκB signaling at a steady state.Exp Hematol. 2025 Apr;144:104730. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2025.104730. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Exp Hematol. 2025. PMID: 39900173
-
The reprogramming factor KLF4 in normal and malignant blood cells.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 16;16:1584181. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1584181. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40589762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylation of KLF5 maintains EMT and tumorigenicity to cause chemoresistant bone metastasis in prostate cancer.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 17;12(1):1714. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21976-w. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33731701 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor (KLF)5: An emerging foe of cardiovascular health.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022 Feb;163:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 13. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34653523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evans MJ, Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292(5819):154–156. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

