Vasopressor use as a surrogate for post-intubation hemodynamic instability is associated with in-hospital and 90-day mortality: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 26374289
- PMCID: PMC4572685
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-015-1410-7
Vasopressor use as a surrogate for post-intubation hemodynamic instability is associated with in-hospital and 90-day mortality: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Evidence is lacking for what defines post-intubation hypotension in the intensive care unit (ICU). If a valid definition could be used, the potential exists to evaluate possible risk factors and thereby improve post-intubation. Thus, our objectives were to arrive at the best surrogate for post-intubation hypotension that accurately predicts both in-hospital and 90-day mortality in a population of ICU patients and to report mortality rates between the exposed and unexposed cohorts.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of emergent endotracheal intubations in a medical-surgical ICU from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2011 to evaluate surrogates for post-intubation hypotension that would predict in-hospital and 90-day mortality followed by an analysis of exposed versus unexposed using our best surrogate. Patients were ≥18 years of age, underwent emergent intubation during their first ICU admission, and did not meet any of the surrogates 60 min pre-intubation.
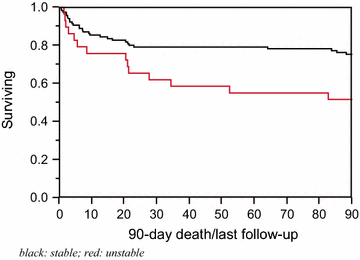
Results: The six surrogates evaluated 60 min post-intubation were those with any systolic blood pressures ≤90 mmHg, any mean arterial pressures ≤65 mmHg, reduction in median systolic blood pressures of ≥20%, any vasopressor administration, any non-sinus rhythm and, fluid administration of ≥30 ml/kg. A total of 147 patients were included. Of the six surrogates, only the administration of any vasopressor 60 min post-intubation remained significant for mortality. Twenty-nine patients were then labeled as hemodynamically unstable and compared to the 118 patients labeled as hemodynamically stable. After adjusting for confounders, the hemodynamically unstable group had a significantly higher in-hospital and 90-day mortality [OR (95% CI); 3.84 (1.31-11.57) (p value = 0.01) and 2.37 (1.18-4.61) (p-value = 0.02)].
Conclusions: Emergently intubated patients manifesting hemodynamic instability after but not before intubation, as measured by vasoactive administration 60 min post-intubation, have a higher association with in-hospital and 90-day mortality.
Figures

References
-
- Jaber S, Amraoui J, Lefrant JY, Arich C, Cohendy R, Landreau L, Calvet Y, Capdevila X, Mahamat A, Eledjam JJ. Clinical practice and risk factors for immediate complications of endotracheal intubation in the intensive care unit: a prospective, multiple-center study. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:2355–2361. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000233879.58720.87. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

