Effect of Extended-Release Niacin on High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Functionality, Lipoprotein Metabolism, and Mediators of Vascular Inflammation in Statin-Treated Patients
- PMID: 26374297
- PMCID: PMC4599486
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001508
Effect of Extended-Release Niacin on High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Functionality, Lipoprotein Metabolism, and Mediators of Vascular Inflammation in Statin-Treated Patients
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to explore the influence of extended-release niacin/laropiprant (ERN/LRP) versus placebo on high-density lipoprotein (HDL) antioxidant function, cholesterol efflux, apolipoprotein B100 (apoB)-containing lipoproteins, and mediators of vascular inflammation associated with 15% increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Study patients had persistent dyslipidemia despite receiving high-dose statin treatment.
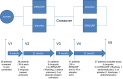
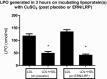
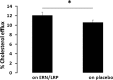
Methods and results: In a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial, we compared the effect of ERN/LRP with placebo in 27 statin-treated dyslipidemic patients who had not achieved National Cholesterol Education Program-ATP III targets for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). We measured fasting lipid profile, apolipoproteins, cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) activity, paraoxonase 1 (PON1) activity, small dense LDL apoB (sdLDL-apoB), oxidized LDL (oxLDL), glycated apoB (glyc-apoB), lipoprotein phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2), lysophosphatidyl choline (lyso-PC), macrophage chemoattractant protein (MCP1), serum amyloid A (SAA) and myeloperoxidase (MPO). We also examined the capacity of HDL to protect LDL from in vitro oxidation and the percentage cholesterol efflux mediated by apoB depleted serum. ERN/LRP was associated with an 18% increase in HDL-C levels compared to placebo (1.55 versus 1.31 mmol/L, P<0.0001). There were significant reductions in total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, total serum apoB, lipoprotein (a), CETP activity, oxLDL, Lp-PLA2, lyso-PC, MCP1, and SAA, but no significant changes in glyc-apoB or sdLDL-apoB concentration. There was a modest increase in cholesterol efflux function of HDL (19.5%, P=0.045), but no change in the antioxidant capacity of HDL in vitro or PON1 activity.
Conclusions: ERN/LRP reduces LDL-associated mediators of vascular inflammation, but has varied effects on HDL functionality and LDL quality, which may counter its HDL-C-raising effect.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01054508.
Keywords: HDL functionality; LDL quality; cholesterol efflux; extended‐release niacin; inflammation; laropiprant; oxidation.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of extended-release niacin/laropiprant, simvastatin, and the combination on correlations between apolipoprotein B, LDL cholesterol, and non-HDL cholesterol in patients with dyslipidemia.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014 May 7;10:279-90. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S58694. eCollection 2014. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014. PMID: 24855368 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of extended-release niacin on the postprandial metabolism of Lp(a) and ApoB-100-containing lipoproteins in statin-treated men with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Dec;35(12):2686-93. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306136. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26515419 Clinical Trial.
-
Consistency of extended-release niacin/laropiprant effects on Lp(a), ApoB, non-HDL-C, Apo A1, and ApoB/ApoA1 ratio across patient subgroups.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012 Jun 1;12(3):197-206. doi: 10.2165/11631530-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22500948
-
Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review.
-
Niacin-ER/statin combination for the treatment of dyslipidemia: focus on low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2006 Jul;8(7):493-9; quiz 500-1. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2006.05505.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2006. PMID: 16849903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paraoxonase 1 and atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 16;10:1065967. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1065967. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36873390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein B and Cardiovascular Disease: Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target.Metabolites. 2021 Oct 8;11(10):690. doi: 10.3390/metabo11100690. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34677405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe Hypertriglyceridaemia and Chylomicronaemia Syndrome-Causes, Clinical Presentation, and Therapeutic Options.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 30;13(5):621. doi: 10.3390/metabo13050621. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37233662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and future therapies for addressing the effects of inflammation on HDL cholesterol metabolism.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;174(22):3986-4006. doi: 10.1111/bph.13743. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28326542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Symbiotic anti-oxidant, anti-glycation, and anti-inflammatory qualities of a combination of thiamine and niacin protected type-2 diabetic male rats against both macro and micro-vascular complications.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(1):98-104. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.77553.16771. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39877627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller GJ, Miller NE. Plasma-high-density-lipoprotein concentration and development of ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet. 1975;1:16–19. - PubMed
-
- Jafri H, Alsheikh-Ali AA, Karas RH. Meta-analysis: statin therapy does not alter the association between low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and increased cardiovascular risk. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:800–808. - PubMed
-
- Barter P, Gotto AM, LaRosa JC, Maroni J, Szarek M, Grundy SM, Kastelein JJ, Bittner V, Fruchart JC. HDL cholesterol, very low levels of LDL cholesterol, and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1301–1310. - PubMed
-
- Boden WE, Probstfield JL, Anderson T, Chaitman BR, Desvignes-Nickens P, Koprowicz K, McBride R, Teo K, Weintraub W. Niacin in patients with low HDL cholesterol levels receiving intensive statin therapy. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2255–2267. - PubMed
-
- HPS2 THRIVE Group. Landray MJ, Haynes R. Effects of extended-release niacin with laropiprant in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:203–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

