Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces
- PMID: 26374838
- PMCID: PMC4593075
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1511027112
Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces
Abstract
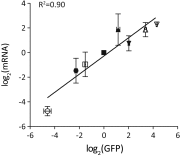
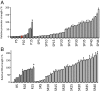
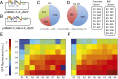
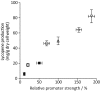
There is a great demand for precisely quantitating the expression of genes of interest in synthetic and systems biotechnology as new and fascinating insights into the genetics of streptomycetes have come to light. Here, we developed, for the first time to our knowledge, a quantitative method based on flow cytometry and a superfolder green fluorescent protein (sfGFP) at single-cell resolution in Streptomyces. Single cells of filamentous bacteria were obtained by releasing the protoplasts from the mycelium, and the dead cells could be distinguished from the viable ones by propidium iodide (PI) staining. With this sophisticated quantitative method, some 200 native or synthetic promoters and 200 ribosomal binding sites (RBSs) were characterized in a high-throughput format. Furthermore, an insulator (RiboJ) was recruited to eliminate the interference between promoters and RBSs and improve the modularity of regulatory elements. Seven synthetic promoters with gradient strength were successfully applied in a proof-of-principle approach to activate and overproduce the cryptic lycopene in a predictable manner in Streptomyces avermitilis. Our work therefore presents a quantitative strategy and universal synthetic modular regulatory elements, which will facilitate the functional optimization of gene clusters and the drug discovery process in Streptomyces.
Keywords: flow cytometry; modular regulatory elements; natural product; single-cell resolution; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ehrlich J, Bartz QR, Smith RM, Joslyn DA, Burkholder PR. Chloromycetin, a new antibiotic from a soil actinomycete. Science. 1947;106(2757):417. - PubMed
-
- Law BK. Rapamycin: An anti-cancer immunosuppressant? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005;56(1):47–60. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Sandiford SK, van Wezel GP. Triggers and cues that activate antibiotic production by actinomycetes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;41(2):371–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

