Crystal structure reveals specific recognition of a G-quadruplex RNA by a β-turn in the RGG motif of FMRP
- PMID: 26374839
- PMCID: PMC4593078
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1515737112
Crystal structure reveals specific recognition of a G-quadruplex RNA by a β-turn in the RGG motif of FMRP
Abstract
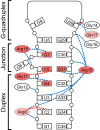
Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein (FMRP) is a regulatory RNA binding protein that plays a central role in the development of several human disorders including Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) and autism. FMRP uses an arginine-glycine-rich (RGG) motif for specific interactions with guanine (G)-quadruplexes, mRNA elements implicated in the disease-associated regulation of specific mRNAs. Here we report the 2.8-Å crystal structure of the complex between the human FMRP RGG peptide bound to the in vitro selected G-rich RNA. In this model system, the RNA adopts an intramolecular K(+)-stabilized G-quadruplex structure composed of three G-quartets and a mixed tetrad connected to an RNA duplex. The RGG peptide specifically binds to the duplex-quadruplex junction, the mixed tetrad, and the duplex region of the RNA through shape complementarity, cation-π interactions, and multiple hydrogen bonds. Many of these interactions critically depend on a type I β-turn, a secondary structure element whose formation was not previously recognized in the RGG motif of FMRP. RNA mutagenesis and footprinting experiments indicate that interactions of the peptide with the duplex-quadruplex junction and the duplex of RNA are equally important for affinity and specificity of the RGG-RNA complex formation. These results suggest that specific binding of cellular RNAs by FMRP may involve hydrogen bonding with RNA duplexes and that RNA duplex recognition can be a characteristic RNA binding feature for RGG motifs in other proteins.
Keywords: FMRP; G-quadruplex; RGG box; RNA structure; fragile X syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
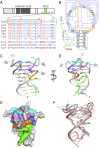

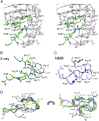
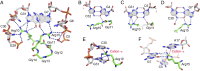
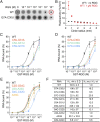

References
-
- Baltz AG, et al. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Mol Cell. 2012;46(5):674–690. - PubMed
-
- Castello A, et al. Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell. 2012;149(6):1393–1406. - PubMed
-
- Ashley CT, Jr, Wilkinson KD, Reines D, Warren ST. FMR1 protein: Conserved RNP family domains and selective RNA binding. Science. 1993;262(5133):563–566. - PubMed
-
- De Boulle K, et al. A point mutation in the FMR-1 gene associated with fragile X mental retardation. Nat Genet. 1993;3(1):31–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

