BCL11A enhancer dissection by Cas9-mediated in situ saturating mutagenesis
- PMID: 26375006
- PMCID: PMC4644101
- DOI: 10.1038/nature15521
BCL11A enhancer dissection by Cas9-mediated in situ saturating mutagenesis
Abstract
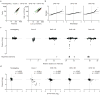
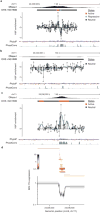
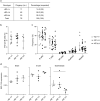
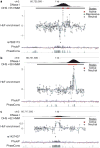
Enhancers, critical determinants of cellular identity, are commonly recognized by correlative chromatin marks and gain-of-function potential, although only loss-of-function studies can demonstrate their requirement in the native genomic context. Previously, we identified an erythroid enhancer of human BCL11A, subject to common genetic variation associated with the fetal haemoglobin level, the mouse orthologue of which is necessary for erythroid BCL11A expression. Here we develop pooled clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-Cas9 guide RNA libraries to perform in situ saturating mutagenesis of the human and mouse enhancers. This approach reveals critical minimal features and discrete vulnerabilities of these enhancers. Despite conserved function of the composite enhancers, their architecture diverges. The crucial human sequences appear to be primate-specific. Through editing of primary human progenitors and mouse transgenesis, we validate the BCL11A erythroid enhancer as a target for fetal haemoglobin reinduction. The detailed enhancer map will inform therapeutic genome editing, and the screening approach described here is generally applicable to functional interrogation of non-coding genomic elements.
Figures











References
-
- Banerji J, Rusconi S, Schaffner W. Expression of a β-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981;27:299–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL119099/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK093705/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL032259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110049/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG008171/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL032262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL032262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99-HG008171/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG005085/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01-DK097768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08DK093705/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F30DK103359-01A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK049216/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL119099/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5DP1-MH100706/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- P30 DK049216/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG008399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DP1 MH100706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 A1084905/PHS HHS/United States
- R01HG005085/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99HG008399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK103359/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

