The Search for a Volatile Human Specific Marker in the Decomposition Process
- PMID: 26375029
- PMCID: PMC4572707
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137341
The Search for a Volatile Human Specific Marker in the Decomposition Process
Abstract
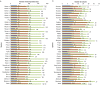
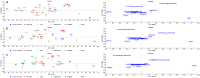
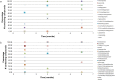
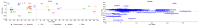
In this study, a validated method using a thermal desorber combined with a gas chromatograph coupled to mass spectrometry was used to identify the volatile organic compounds released during decomposition of 6 human and 26 animal remains in a laboratory environment during a period of 6 months. 452 compounds were identified. Among them a human specific marker was sought using principle component analysis. We found a combination of 8 compounds (ethyl propionate, propyl propionate, propyl butyrate, ethyl pentanoate, pyridine, diethyl disulfide, methyl(methylthio)ethyl disulfide and 3-methylthio-1-propanol) that led to the distinction of human and pig remains from other animal remains. Furthermore, it was possible to separate the pig remains from human remains based on 5 esters (3-methylbutyl pentanoate, 3-methylbutyl 3-methylbutyrate, 3-methylbutyl 2-methylbutyrate, butyl pentanoate and propyl hexanoate). Further research in the field with full bodies has to corroborate these results and search for one or more human specific markers. These markers would allow a more efficiently training of cadaver dogs or portable detection devices could be developed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Brasseur C, Dekeirsschieter J, Schotsmans EM, de Koning S, Wilson AS, Haubruge E, et al. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the forensic study of cadaveric volatile organic compounds released in soil by buried decaying pig carcasses. Journal of chromatography A. 2012;1255:163–70. 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.03.048 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

