A nested phosphorus and proton coil array for brain magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
- PMID: 26375209
- PMCID: PMC4651763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.08.066
A nested phosphorus and proton coil array for brain magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
Abstract
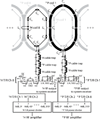
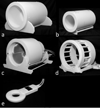
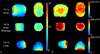
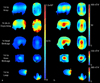
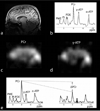
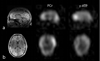
A dual-nuclei radiofrequency coil array was constructed for phosphorus and proton magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of the human brain at 7T. An eight-channel transceive degenerate birdcage phosphorus module was implemented to provide whole-brain coverage and significant sensitivity improvement over a standard dual-tuned loop coil. A nested eight-channel proton module provided adequate sensitivity for anatomical localization without substantially sacrificing performance on the phosphorus module. The developed array enabled phosphorus spectroscopy, a saturation transfer technique to calculate the global creatine kinase forward reaction rate, and single-metabolite whole-brain imaging with 1.4cm nominal isotropic resolution in 15min (2.3cm actual resolution), while additionally enabling 1mm isotropic proton imaging. This study demonstrates that a multi-channel array can be utilized for phosphorus and proton applications with improved coverage and/or sensitivity over traditional single-channel coils. The efficient multi-channel coil array, time-efficient pulse sequences, and the enhanced signal strength available at ultra-high fields can be combined to allow volumetric assessment of the brain and could provide new insights into the underlying energy metabolism impairment in several neurodegenerative conditions, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, as well as mental disorders such as schizophrenia.
Keywords: Creatine kinase reaction; Degenerate birdcage; Dual-tuned coil; FLORET pulse sequence; Transceive phased array.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A birdcage transmit, 24-channel conformal receive array coil for sensitive 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of the human brain at 7 T.NMR Biomed. 2024 Oct;37(10):e5178. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5178. Epub 2024 May 24. NMR Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38784970
-
A flexible nested sodium and proton coil array with wideband matching for knee cartilage MRI at 3T.Magn Reson Med. 2016 Oct;76(4):1325-34. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26017. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Magn Reson Med. 2016. PMID: 26502310 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a nested eight-channel sodium and four-channel proton coil for 7T knee imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2013 Jul;70(1):259-68. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24432. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Magn Reson Med. 2013. PMID: 22887123 Free PMC article.
-
Theory and application of array coils in MR spectroscopy.NMR Biomed. 1997 Dec;10(8):394-410. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-1492(199712)10:8<394::aid-nbm494>3.0.co;2-0. NMR Biomed. 1997. PMID: 9542737 Review.
-
The state-of-the-art and emerging design approaches of double-tuned RF coils for X-nuclei, brain MR imaging and spectroscopy: A review.Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Oct;72:103-116. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32653426 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel multifrequency-tuned transceiver array for human-brain 31P-MRSI at 7 T.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Jun;93(6):2640-2654. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30449. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 39902517 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of high-channel count, switch matrices for multinuclear, high-field MRI.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 17;15(8):e0237494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237494. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32804972 Free PMC article.
-
A radially interleaved sodium and proton coil array for brain MRI at 7 T.NMR Biomed. 2021 Dec;34(12):e4608. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4608. Epub 2021 Sep 3. NMR Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34476861 Free PMC article.
-
A Quantitative Comparison of 31P Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy RF Coil Sensitivity and SNR between 7T and 10.5T Human MRI Scanners Using a Loop-Dipole 31P-1H Probe.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 6;24(17):5793. doi: 10.3390/s24175793. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39275704 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Phosphocreatine and Determination of BOLD Kinetics in Lower Extremity Muscles using a Dual-Frequency Coil Array.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 28;6:30568. doi: 10.1038/srep30568. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27465636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackerman JJ, Grove TH, Wong GG, Gadian DG, Radda GK. Mapping of metabolites in whole animals by 31P NMR using surface coils. Nature. 1980;283:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Adriany G, Gruetter R. A half-volume coil for efficient proton decoupling in humans at 4 tesla. J Magn Reson. 1997;125:178–184. - PubMed
-
- Alagappan V, Nistler J, Adalsteinsson E, Setsompop K, Fontius U, Zelinski A, Vester M, Wiggins GC, Hebrank F, Renz W, Schmitt F, Wald LL. Degenerate mode band-pass birdcage coil for accelerated parallel excitation. Magn Reson Med. 2007;57:1148–1158. - PubMed
-
- Alecci M, Romanzetti S, Kaffanke J, Celik A, Wegener HP, Shah NJ. Practical design of a 4 Tesla double-tuned RF surface coil for interleaved 1H and 23Na MRI of rat brain. J Magn Reson. 2006;181:203–211. - PubMed
-
- Alger JR, Shulman RG. NMR studies of enzymatic rates in vitro and in vivo by magnetization transfer. Q Rev Biophys. 1984;17:83–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

