Black women's hair: the main scalp dermatoses and aesthetic practices in women of African ethnicity
- PMID: 26375213
- PMCID: PMC4560533
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152845
Black women's hair: the main scalp dermatoses and aesthetic practices in women of African ethnicity
Abstract
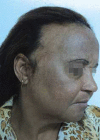
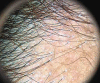
Afro-ethnic hair is different from Caucasian and Asian hair and has unique features. Ethnic hair is more prone to certain conditions or diseases. Such diseases are not only related to the fragile inner structure of the hair, but also to the cultural habits of hairstyles that often exert traction forces upon the pilosebaceous follicle. Women with African hair subject their hair to chemical treatments such as hair straightening and relaxing, and thus modify the structure of their hair shaft, making it more susceptible to damage. For this reason, hair complaints are common among black women and represent a diagnostic challenge to the dermatologist, requiring a thorough clinical examination of the hair and scalp, and a detailed medical history of the patient. The purpose of this review is to warn of the potential side effects and sequelae related to hairstyles and hair treatments used by black women, and to highlight the major diseases that affect this ethnicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None
Figures


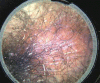
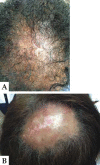

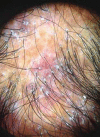
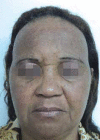


References
-
- Franbourg A, Hallegot P, Baltenneck F, Toutain C, Leroy F. Current research on ethnic hair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:S115–S119. - PubMed
-
- Alchorne MM, de Abreu MA. Dermatology in black skin. An Bras Dermatol. 2008;83:7–20. - PubMed
-
- Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffiths C, editors. Rook's Textbook of Dermatology. 8th ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010.
-
- Blume-Peytavi U, Tosti A, Whiting DA, Trüeb RM. Hair Growth and Disorders. Berlin: Springer; 2008.
-
- Miteva M, Tosti A. A detective look' at hair biopsies from African-American patients. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1289–1294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
