Vascular structures in dermoscopy
- PMID: 26375224
- PMCID: PMC4560544
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153452
Vascular structures in dermoscopy
Abstract
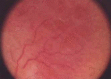
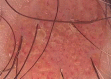
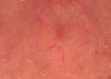
Dermoscopy is an aiding method in the visualization of the epidermis and dermis. It is usually used to diagnose melanocytic lesions. In recent years, dermoscopy has increasingly been used to diagnose non-melanocytic lesions. Certain vascular structures, their patterns of arrangement and additional criteria may demonstrate lesion-specific characteristics. In this review, vascular structures and their arrangements are discussed separately in the light of conflicting views and an overview of recent literature.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures



References
-
- Arrazola P, Mullani NA, Abramovits W. DermLite II: an innovative portable instrument for dermoscopy without the need of immersion fluids. Skinmed. 2005;4:78–83. - PubMed
-
- Zalaudek I, Kreusch J, Giacomel J, Ferrara G, Catricalà C, Argenziano G. How to diagnose nonpigmented skin tumors: A review of vascular structures seen with dermoscopy. Part I. Melanocytic skin tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:361–374. - PubMed
-
- Wang SQ, Dusza SW, Scope A, Braun RP, Kopf AW, Marghoob AA. Differences in dermoscopic images from nonpolarized dermoscope and polarized dermoscope influence the diagnostic accuracy and confidence level: a pilot study. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:1389–1395. - PubMed
-
- Kreusch J, Koch F. Incident light microscopic characterization of vascular patterns in skin tumors. Hautarzt. 1996;47:264–272. - PubMed
-
- Argenziano G, Zalaudek I, Corona R, Sera F, Cicale L, Petrillo G, et al. Vascular structures in skin tumors. A dermoscopy study. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:1485–1489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
