Epigallocatechin gallate affects glucose metabolism and increases fitness and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 26375250
- PMCID: PMC4741552
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5215
Epigallocatechin gallate affects glucose metabolism and increases fitness and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
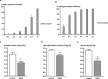
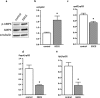
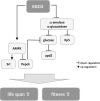
In this study, we tested whether a standardized epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) rich green tea extract (comprising > 90% EGCG) affects fitness and lifespan as well as parameters of glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster. Following the application of the green tea extract a significant increase in the mean lifespan (+ 3.3 days) and the 50% survival (+ 4.3 days) as well as improved fitness was detected. These effects went along an increased expression of Spargel, the homolog of mammalian PGC1α, which has been reported to affect lifespan in flies. Intriguingly, in flies, treatment with the green tea extract decreased glucose concentrations, which were accompanied by an inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity. Computational docking analysis proved the potential of EGCG to dock into the substrate binding pocket of α-amylase and to a greater extent into α-glucosidase. Furthermore, we demonstrate that EGCG downregulates insulin-like peptide 5 and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, major regulators of glucose metabolism, as well as the Drosophila homolog of leptin, unpaired 2. We propose that a decrease in glucose metabolism in connection with an upregulated expression of Spargel contribute to the better fitness and the extended lifespan in EGCG-treated flies.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; Gerotarget; epigallocathechin-3-gallate; green tea; life span.
Conflict of interest statement
Manfred Eggersdorfer is an employee of DSM Nutritional Products, Basel, Switzerland and provided funding for this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits starch digestion and improves glucose homeostasis through direct or indirect activation of PXR/CAR-mediated phase II metabolism in diabetic mice.Food Funct. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):4651-4663. doi: 10.1039/c8fo01293h. Food Funct. 2018. PMID: 30183039
-
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) alters body fat and lean mass through sex-dependent metabolic mechanisms in Drosophila melanogaster.Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2019 Dec;70(8):959-969. doi: 10.1080/09637486.2019.1602113. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31010351
-
Epigallocatechin gallate from green tea (Camellia sinensis) increases lifespan and stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans.Planta Med. 2009 Feb;75(3):216-21. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1088378. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Planta Med. 2009. PMID: 19085685
-
A literature review of flavonoids and lifespan in model organisms.Proc Nutr Soc. 2017 May;76(2):145-162. doi: 10.1017/S0029665116000720. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Proc Nutr Soc. 2017. PMID: 27609098 Review.
-
Molecular Targets of Epigallocatechin-Gallate (EGCG): A Special Focus on Signal Transduction and Cancer.Nutrients. 2018 Dec 6;10(12):1936. doi: 10.3390/nu10121936. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30563268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pterocarpus marsupium extract extends replicative lifespan in budding yeast.Geroscience. 2021 Oct;43(5):2595-2609. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00418-x. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Geroscience. 2021. PMID: 34297314 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Behind Organ-Related Aging and Regulatory Effects of Natural Therapeutics.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01792-5. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40528054 Review.
-
Inhibition of histone acetyltransferase GCN5 extends lifespan in both yeast and human cell lines.Aging Cell. 2020 Apr;19(4):e13129. doi: 10.1111/acel.13129. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 32157780 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Resveratrol Does Not Affect Life Span, Body Composition, Stress Response, and Longevity-Related Gene Expression in Drosophila melanogaster.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 11;19(1):223. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010223. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29324667 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Insights on Caloric Restriction Mimetics for Mitigating Brain Aging and Related Neurodegeneration.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct 16;44(1):67. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01493-2. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39412683 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boon N. Health potential for functional green teas? Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2008;78:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Wu D, Guo Z, Ren Z, Guo W, Meydani SN. Green tea EGCG suppresses T cell proliferation through impairment of IL-2/IL-2 receptor signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;47:636–643. - PubMed
-
- Yan J, Zhao Y, Suo S, Liu Y, Zhao B. Green tea catechins ameliorate adipose insulin resistance by improving oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52:1648–1657. - PubMed
-
- Rains TM, Agarwal S, Maki KC. Antiobesity effects of green tea catechins: a mechanistic review. J Nutr Biochem. 2011;22:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

