Novel application of luciferase assay for the in vitro functional assessment of KAL1 variants in three females with septo-optic dysplasia (SOD)
- PMID: 26375424
- PMCID: PMC4646839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.09.010
Novel application of luciferase assay for the in vitro functional assessment of KAL1 variants in three females with septo-optic dysplasia (SOD)
Abstract
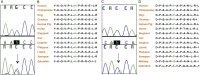
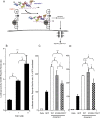
KAL1 is implicated in 5% of Kallmann syndrome cases, a disorder which genotypically overlaps with septo-optic dysplasia (SOD). To date, a reporter-based assay to assess the functional consequences of KAL1 mutations is lacking. We aimed to develop a luciferase assay for novel application to functional assessment of rare KAL1 mutations detected in a screen of 422 patients with SOD. Quantitative analysis was performed using L6-myoblasts stably expressing FGFR1, transfected with a luciferase-reporter vector containing elements of the FGF-responsive osteocalcin promoter. The two variants assayed [p.K185N, p.P291T], were detected in three females with SOD (presenting with optic nerve hypoplasia, midline and pituitary defects). Our novel assay revealed significant decreases in transcriptional activity [p.K185N: 21% (p < 0.01); p.P291T: 40% (p < 0.001)]. Our luciferase-reporter assay, developed for assessment of KAL1 mutations, determined that two variants in females with hypopituitarism/SOD are loss-of-function; demonstrating that this assay is suitable for quantitative assessment of mutations in this gene.
Keywords: Females; KAL1; Kallmann syndrome; Luciferase assay; Septo-optic dysplasia.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic overlap in Kallmann syndrome, combined pituitary hormone deficiency, and septo-optic dysplasia.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Apr;97(4):E694-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2938. Epub 2012 Feb 8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22319038 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical assessment and mutation analysis of Kallmann syndrome 1 (KAL1) and fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1, or KAL2) in five families and 18 sporadic patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Mar;89(3):1079-88. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030476. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15001591
-
HESX1 mutations are an uncommon cause of septooptic dysplasia and hypopituitarism.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Feb;92(2):691-7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1609. Epub 2006 Dec 5. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17148560
-
Septo-optic dysplasia and other midline defects: the role of transcription factors: HESX1 and beyond.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Feb;25(1):115-24. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2010.06.008. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21396578 Review.
-
Genetics of septo-optic dysplasia.Pituitary. 2007;10(4):393-407. doi: 10.1007/s11102-007-0055-5. Pituitary. 2007. PMID: 17587179 Review.
Cited by
-
Anosmin-1-Like Effect of UMODL1/Olfactorin on the Chemomigration of Mouse GnRH Neurons and Zebrafish Olfactory Axons Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 11;10:836179. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.836179. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35223856 Free PMC article.
-
Appetite- and Weight-Regulating Neuroendocrine Circuitry in Hypothalamic Obesity.Endocr Rev. 2024 May 7;45(3):309-342. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad033. Endocr Rev. 2024. PMID: 38019584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Congenital Hypopituitarism During the Neonatal Period: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Therapeutic Options, and Outcome.Front Pediatr. 2021 Feb 2;8:600962. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.600962. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33634051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Identification of Pathogenic Gene Variants in Patients With Neuroendocrine Disorders.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jun 16;106(7):1956-1976. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab177. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33729509 Free PMC article.
-
A rare combination of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, GH deficiency and rectal atresia in a female with an FGFR1 variant: a case report and systematic review of the literature.Endocrine. 2025 Aug;89(2):556-564. doi: 10.1007/s12020-025-04261-4. Epub 2025 May 28. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 40434549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canto P., Munguia P., Söderlund D., Castro J.J., Mendez J.P. Genetic analysis in patients with Kallmann syndrome: coexistence of mutations in prokineticin receptor 2 and KAL1. J. Androl. 2009;30:41–45. - PubMed
-
- del Castillo I., Cohen-Salmon M., Blachard S., Lutfalla G., Petit C. Structure of the X-linked Kallmann syndrome gene and its homologous pseudogene on the Y chromosome. Nat. Genet. 1992;2:305–310. - PubMed
-
- Dhahbi J.M., Spindler S.R., Atamna H., Boffelli D., Mote P., Martin D.I. 5′ YRNA fragments derived by processing of transcripts from specific YRNA genes and pseudogenes are abundant in human serum and plasma. Physiol. Genomics. 2013;45:990–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

