Use of Medical Therapy and Success of Laser Surgery and Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- PMID: 26375848
- PMCID: PMC4698045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2015.07.019
Use of Medical Therapy and Success of Laser Surgery and Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Abstract
Objective: To assess the impact of surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) on use of medication (5-alpha reductase inhibitors, alpha blockers, antispasmodics), we assessed preoperative and postoperative medication utilization among surgically treated men.
Patients and methods: Using the Truven Health Analytics MarketScan Commercial Claims Database, we defined a cohort of men aged <65 years who had surgical therapy for BPH with either transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser procedures from 2007 through 2009. Primary outcomes included freedom from medical or surgical intervention by 4 months after surgery (chi-square and multivariable logistic regression) and subsequent use of medical or surgical intervention in initial responders (Kaplan-Meier and multivariable Cox regression).
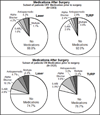
Results: We identified 6430 patients treated with either TURP (3096) or laser procedure (3334) for BPH. Presurgical antispasmodic use was associated with the highest risk of medication use at 4 months after surgery (odds ratio, 5.19; 95% confidence interval (CI), 3.16-8.53 vs no medication use before surgery). At 3 years after surgery, 6% (95% CI, 4%-8%) of laser-treated and 4% (95% CI, 2%-5%) of TURP-treated patients had repeat surgical intervention, and both laser- and TURP-treated patients had an estimated new use of medication rate of 22% (95% CI, 18%-25% laser and 20%-25% TURP). The strongest predictor of intervention after surgery was preoperative antispasmodic use (hazard ratio, 2.49; 95% CI, 1.41-4.43).
Conclusion: Our results show a need for effective patient counseling about continued or new use of medical therapy after laser and TURP procedures. However, most patients experience durable improvement after surgical intervention for BPH.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Yu X, Elliott SP, Wilt TJ, McBean AM. Practice patterns in benign prostatic hyperplasia surgical therapy: the dramatic increase in minimally invasive technologies. J Urol. 2008;180:241–245. discussion 245. - PubMed
-
- Te AE, Malloy TR, Stein BS, Ulchaker JC, Nseyo UO, Hai MA, Malek RS. Photoselective vaporization of the prostate for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: 12-month results from the first United States multicenter prospective trial. J Urol. 2004;172:1404–1408. - PubMed
-
- Ahyai SA, Gilling P, Kaplan SA, Kuntz RM, Madersbacher S, Montorsi F, Speakman MJ, Stief CG. Meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic enlargement. Eur Urol. 2010;58:384–397. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann A, Tubaro A, Barber N, d'Ancona F, Muir G, Witzsch U, Grimm MO, Benejam J, Stolzenburg JU, Riddick A, et al. 180-W XPS GreenLight laser vaporisation versus transurethral resection of the prostate for the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction: 6-month safety and efficacy results of a European Multicentre Randomised Trial--the GOLIATH study. Eur Urol. 2014;65:931–942. - PubMed
-
- Cornu JN, Ahyai S, Bachmann A, de la Rosette J, Gilling P, Gratzke C, McVary K, Novara G, Woo H, Madersbacher S. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Functional Outcomes and Complications Following Transurethral Procedures for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Resulting from Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Update. Eur Urol. 2015;67:1066–1096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

