A Single Oral Administration of Theaflavins Increases Energy Expenditure and the Expression of Metabolic Genes
- PMID: 26375960
- PMCID: PMC4574049
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137809
A Single Oral Administration of Theaflavins Increases Energy Expenditure and the Expression of Metabolic Genes
Abstract
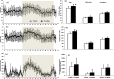
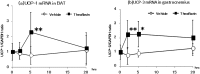
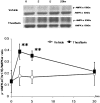
Theaflavins are polyphenols found in black tea, whose physiological activities are not well understood. This study on mice evaluated the influence of a single oral administration of theaflavins on energy metabolism by monitoring the initial metabolic changess in skeletal muscle and brown adipose tissue (BAT). Oxygen consumption (VO2) and energy expenditure (EE) were increased significantly in mice treated with theaflavin rich fraction (TF) compared with the group administered vehicle alone. There was no difference in locomotor activity. Fasting mice were euthanized under anesthesia before and 2 and 5, 20-hr after treatment with TF or vehicle. The mRNA levels of uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) in BAT were increased significantly 2-hr after administration ofTF. The levels of UCP-3 and PGC-1α in the gastrocnemius muscle were increased significantly 2 and 5-hr after administration of TF. The concentration of phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) 1α was also increased significantly in the gastrocnemius 2 and 5-hr after treatment with TF. These results indicate that TF significantly enhances systemic energy expenditure, as evidenced by an increase in expression of metabolic genes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Haslam E. Thoughts on thearubigins. Phytochemistry. 2003;64(1):61–73. Epub 2003/08/30. . - PubMed
-
- Knaze V, Zamora-Ros R, Lujan-Barroso L, Romieu I, Scalbert A, Slimani N, et al. Intake estimation of total and individual flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins and theaflavins, their food sources and determinants in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. The British journal of nutrition. 2012;108(6):1095–108. Epub 2011/12/22. 10.1017/s0007114511006386 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vogiatzoglou A, Mulligan AA, Luben RN, Lentjes MA, Heiss C, Kelm M, et al. Assessment of the dietary intake of total flavan-3-ols, monomeric flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins and theaflavins in the European Union. The British journal of nutrition. 2014;111(8):1463–73. Epub 2013/12/18. 10.1017/s0007114513003930 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

