'Medusa head ataxia': the expanding spectrum of Purkinje cell antibodies in autoimmune cerebellar ataxia. Part 2: Anti-PKC-gamma, anti-GluR-delta2, anti-Ca/ARHGAP26 and anti-VGCC
- PMID: 26377184
- PMCID: PMC4574118
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-015-0357-x
'Medusa head ataxia': the expanding spectrum of Purkinje cell antibodies in autoimmune cerebellar ataxia. Part 2: Anti-PKC-gamma, anti-GluR-delta2, anti-Ca/ARHGAP26 and anti-VGCC
Abstract
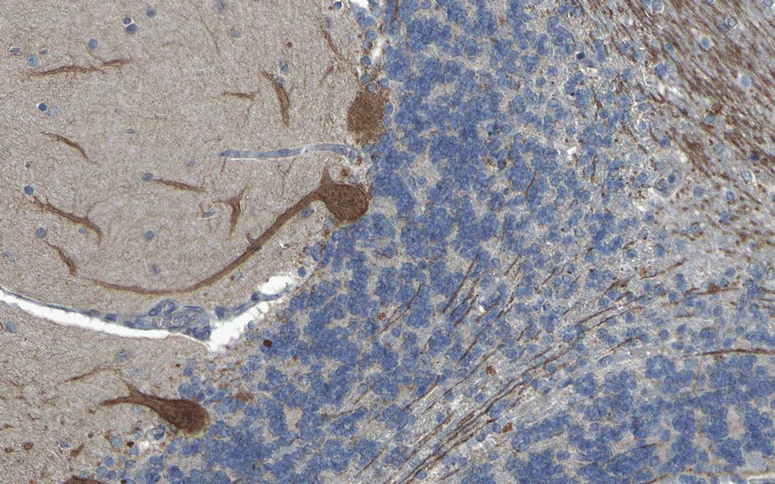
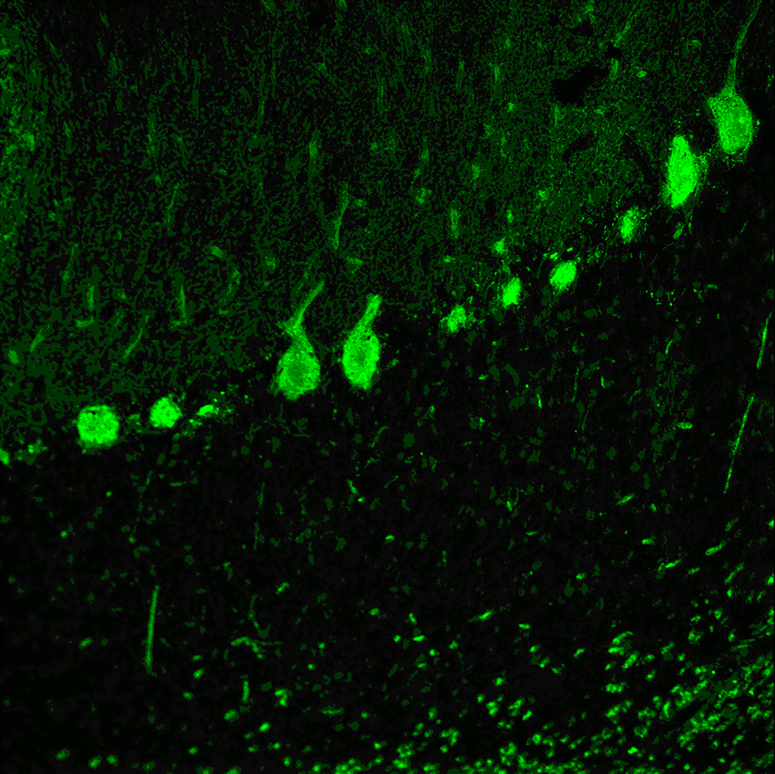
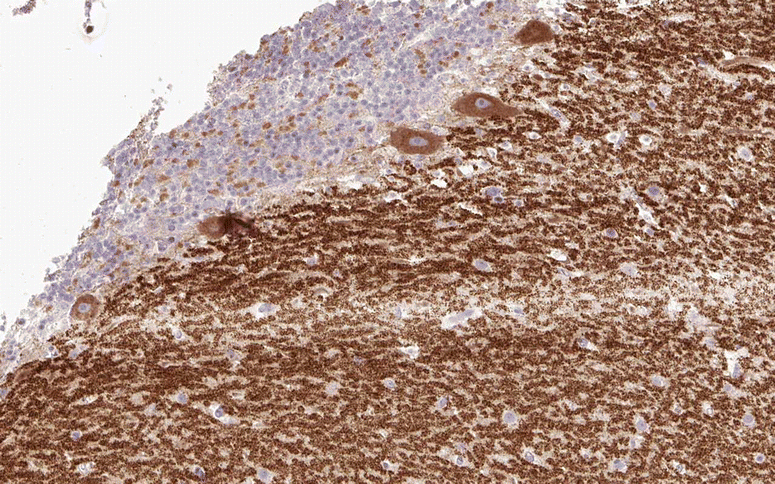
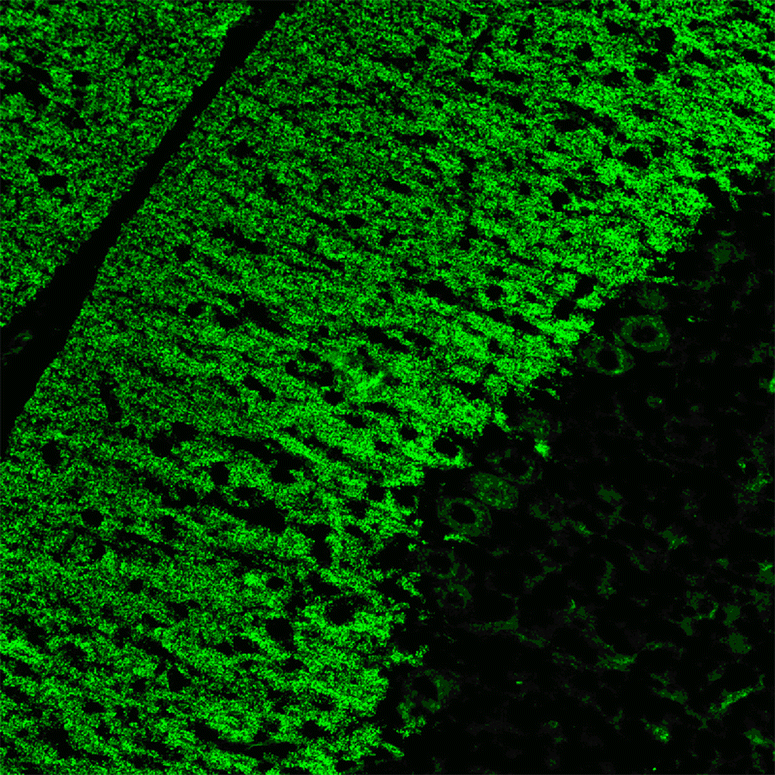
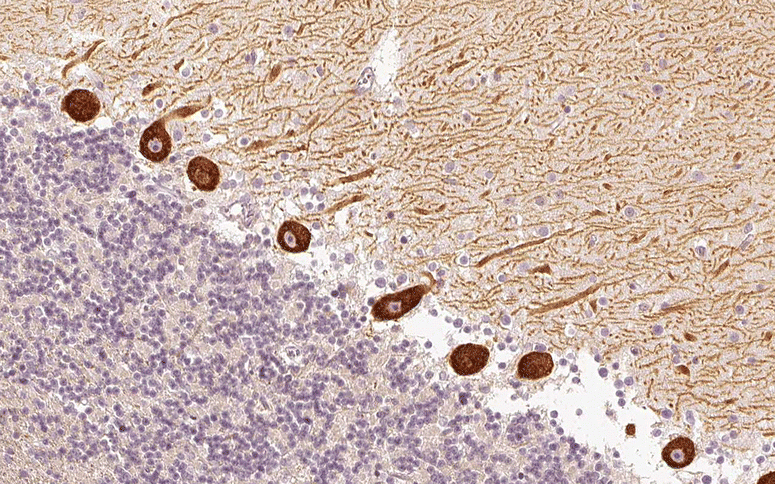
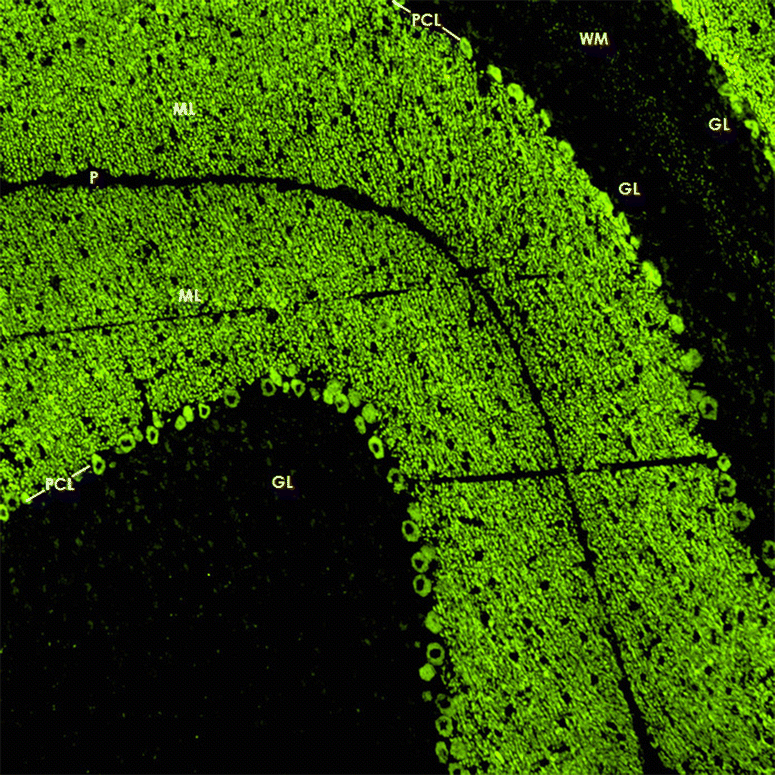
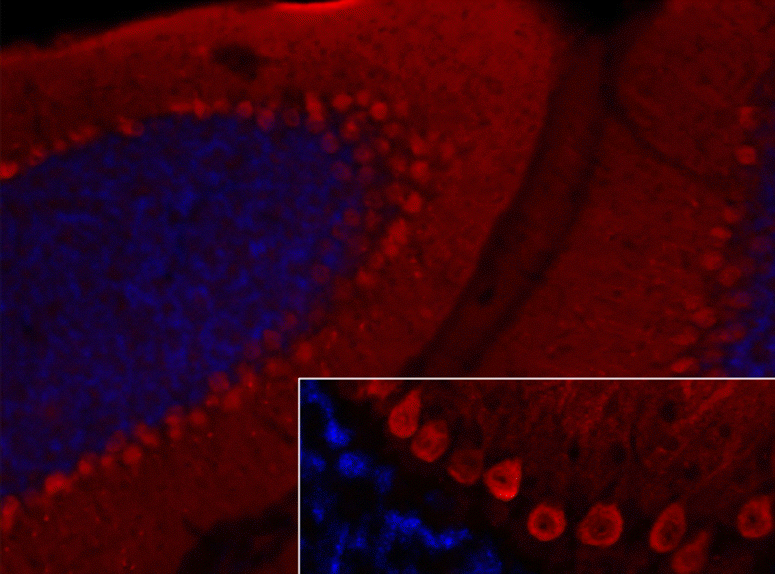
Serological testing for anti-neural autoantibodies is important in patients presenting with idiopathic cerebellar ataxia, since these autoantibodies may indicate cancer, determine treatment and predict prognosis. While some of them target nuclear antigens present in all or most CNS neurons (e.g. anti-Hu, anti-Ri), others more specifically target antigens present in the cytoplasm or plasma membrane of Purkinje cells (PC). In this series of articles, we provide a detailed review of the clinical and paraclinical features, oncological, therapeutic and prognostic implications, pathogenetic relevance, and differential laboratory diagnosis of the 12 most common PC autoantibodies (often referred to as 'Medusa head antibodies' due their characteristic somatodendritic binding pattern when tested by immunohistochemistry). To assist immunologists and neurologists in diagnosing these disorders, typical high-resolution immunohistochemical images of all 12 reactivities are presented, diagnostic pitfalls discussed and all currently available assays reviewed. Of note, most of these antibodies target antigens involved in the mGluR1/calcium pathway essential for PC function and survival. Many of the antigens also play a role in spinocerebellar ataxia. Part 1 focuses on anti-metabotropic glutamate receptor 1-, anti-Homer protein homolog 3-, anti-Sj/inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor- and anti-carbonic anhydrase-related protein VIII-associated autoimmune cerebellar ataxia (ACA); part 2 covers anti-protein kinase C gamma-, anti-glutamate receptor delta-2-, anti-Ca/RhoGTPase-activating protein 26- and anti-voltage-gated calcium channel-associated ACA; and part 3 reviews the current knowledge on anti-Tr/delta notch-like epidermal growth factor-related receptor-, anti-Nb/AP3B2-, anti-Yo/cerebellar degeneration-related protein 2- and Purkinje cell antibody 2-associated ACA, discusses differential diagnostic aspects, and provides a summary and outlook.
Figures
References
-
- Clark AS, West KA, Blumberg PM, Dennis PA. Altered protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms in non-small cell lung cancer cells: PKCdelta promotes cellular survival and chemotherapeutic resistance. Cancer Res. 2003;63:780–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

