The AhR and NF-κB/Rel Proteins Mediate the Inhibitory Effect of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin on the 3' Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Regulatory Region
- PMID: 26377645
- PMCID: PMC5009439
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv193
The AhR and NF-κB/Rel Proteins Mediate the Inhibitory Effect of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin on the 3' Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Regulatory Region
Abstract
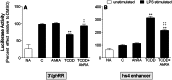
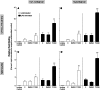
Transcriptional regulation of the murine immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chain gene (Igh) involves several regulatory elements including the 3'Igh regulatory region (3'IghRR), which is composed of at least 4 enhancers (hs3A, hs1.2, hs3B, and hs4). The hs1.2 and hs4 enhancers exhibit the greatest transcriptional activity and contain binding sites for several transcription factors including nuclear factor kappaB/Rel (NF-κB/Rel) proteins and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Interestingly, the environmental immunosuppressant 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), which potently inhibits antibody secretion, also profoundly inhibits 3'IghRR and hs1.2 enhancer activation induced by the B-lymphocyte activator lipopolysaccharide (LPS), but enhances LPS-induced activation of the hs4 enhancer. Within the hs1.2 and hs4 enhancers, the AhR binding site is in close proximity or overlaps an NF-κB/Rel binding site suggesting a potential reciprocal modulation of the 3'IghRR by AhR and NF-κB/Rel. The objective of the current study was to evaluate the role of NF-κB/Rel and the AhR on the 3'IghRR and its enhancers using the AhR ligand TCDD, the AhR antagonist CH223191, and toll-like receptor agonists LPS, Resiquimod (R848), or cytosine-phosphate-guanine-oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG). Utilizing the CH12.LX B-lymphocyte cell line and variants expressing either a 3'IghRR-regulated transgene reporter or an inducible IκBα (inhibitor kappa B-alpha protein) superrepressor (IκBαAA), we demonstrate an AhR- and NF-κB/Rel-dependent modulation of 3'IghRR and hs4 activity. Additionally, in mouse splenocytes or CH12.LX cells, binding within the hs1.2 and hs4 enhancer of the AhR and the NF-κB/Rel proteins RelA and RelB was differentially altered by the cotreatment of LPS and TCDD. These results suggest that the AhR and NF-κB/Rel protein binding profile within the 3'IghRR mediates the inhibitory effects of TCDD on Ig expression and therefore antibody levels.
Keywords: 3′Igh regulatory region; NF-κB/Rel; TCDD; aryl hydrocarbon receptor; gene regulation; immunoglobulin; immunosuppression.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
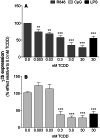
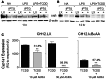
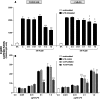
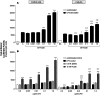
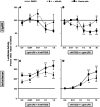



 ). The inhibitory effects of the AhR antagonist (AhRA) and the IκBαAA superrepressor are also illustrated. Nucleotide sequences for the κB (NF-κB/Rel DNA binding motif) (italicized, top arrows) and DRE (dioxin-responsive element) (bottom arrows) motifs are shown for the hs1.2 and hs4 enhancers; arrows indicate the boundary for each binding site.
). The inhibitory effects of the AhR antagonist (AhRA) and the IκBαAA superrepressor are also illustrated. Nucleotide sequences for the κB (NF-κB/Rel DNA binding motif) (italicized, top arrows) and DRE (dioxin-responsive element) (bottom arrows) motifs are shown for the hs1.2 and hs4 enhancers; arrows indicate the boundary for each binding site.Similar articles
-
Diverse chemicals including aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands modulate transcriptional activity of the 3'immunoglobulin heavy chain regulatory region.Toxicology. 2009 Jun 30;261(1-2):9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2009.03.015. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Toxicology. 2009. PMID: 19447539 Free PMC article.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates an essential transcriptional element in the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene.Cell Immunol. 2015 May;295(1):60-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.02.012. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cell Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25749007 Free PMC article.
-
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induces transcriptional activity of the human polymorphic hs1,2 enhancer of the 3'Igh regulatory region.J Immunol. 2012 Apr 1;188(7):3294-306. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101111. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22357631 Free PMC article.
-
A new cross-talk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and RelB, a member of the NF-kappaB family.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Feb 15;77(4):734-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.09.036. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18955032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The long winding road toward understanding the molecular mechanisms for B-cell suppression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Mar;120 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S171-91. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq324. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 20952503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Bone Biology.Int J Tryptophan Res. 2024 May 15;17:11786469241246674. doi: 10.1177/11786469241246674. eCollection 2024. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2024. PMID: 38757095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Connects Inflammation to Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 24;21(15):5264. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155264. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32722276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) beyond the canonical AHR/ARNT signaling pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Feb;208:115371. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115371. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36528068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Murine Coronavirus Infection Activates the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in an Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-Independent Manner, Contributing to Cytokine Modulation and Proviral TCDD-Inducible-PARP Expression.J Virol. 2020 Jan 17;94(3):e01743-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01743-19. Print 2020 Jan 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31694960 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus on the Key Characteristics of Immunotoxic Agents as a Basis for Hazard Identification.Environ Health Perspect. 2022 Oct;130(10):105001. doi: 10.1289/EHP10800. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Environ Health Perspect. 2022. PMID: 36201310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdou A. G., Hanout H. M. (2008). Evaluation of survivin and NF-kappaB in psoriasis, an immunohistochemical study. J. Cutan. Pathol. 35, 445–451. - PubMed
-
- Arnold L. W., LoCascio N. J., Lutz P. M., Pennell C. A., Klapper D., Haughton G. (1983). Antigen-induced lymphomagenesis: Identification of a murine B cell lymphoma with known antigen specificity. J. Immunol. 131, 2064–2068. - PubMed
-
- Ashizawa M., Miyazaki M., Abe K., Furusu A., Isomoto H., Harada T., Ozono Y., Sakai H., Koji T., Kohno S. (2003). Detection of nuclear factor-kappaB in IgA nephropathy using Southwestern histochemistry. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 42, 76–86. - PubMed
-
- Aupetit C., Drouet M., Pinaud E., Denizot Y., Aldigier J. C., Bridoux F., Cogne M. (2000). Alleles of the alpha1 immunoglobulin gene 3′ enhancer control evolution of IgA nephropathy toward renal failure. Kidney Int. 58, 966–971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

