An intact helical domain is required for Gα14 to stimulate phospholipase Cβ
- PMID: 26377666
- PMCID: PMC4573470
- DOI: 10.1186/s12900-015-0043-3
An intact helical domain is required for Gα14 to stimulate phospholipase Cβ
Abstract
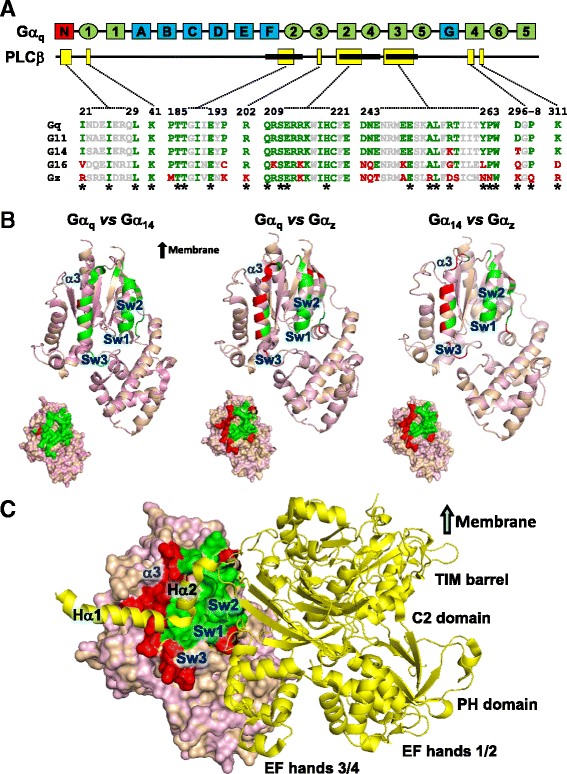
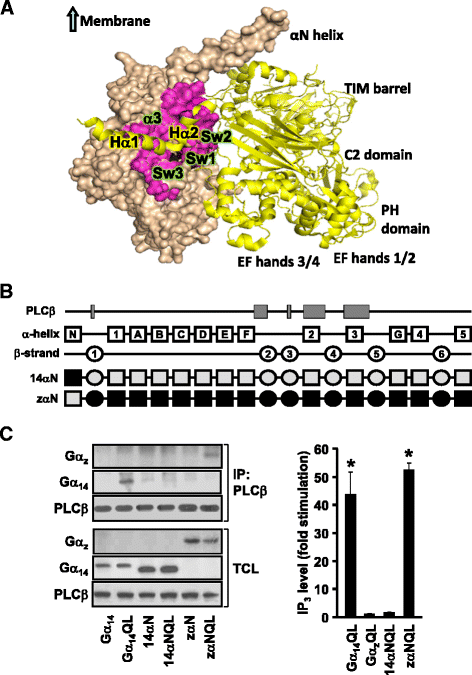
Background: Stimulation of phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ) by the activated α-subunit of Gq (Gαq) constitutes a major signaling pathway for cellular regulation, and structural studies have recently revealed the molecular interactions between PLCβ and Gαq. Yet, most of the PLCβ-interacting residues identified on Gαq are not unique to members of the Gαq family. Molecular modeling predicts that the core PLCβ-interacting residues located on the switch regions of Gαq are similarly positioned in Gαz which does not stimulate PLCβ. Using wild-type and constitutively active chimeras constructed between Gαz and Gα14, a member of the Gαq family, we examined if the PLCβ-interacting residues identified in Gαq are indeed essential.
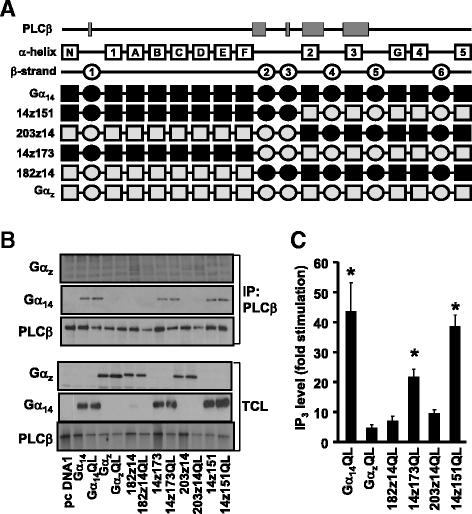
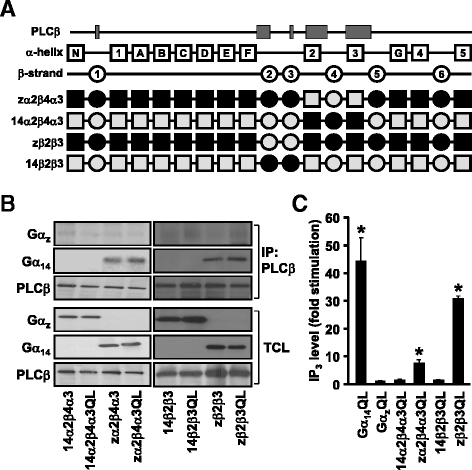
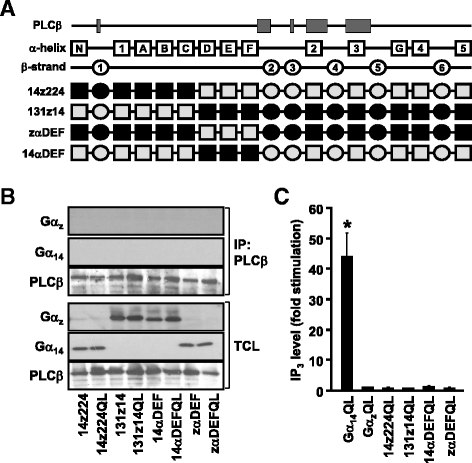
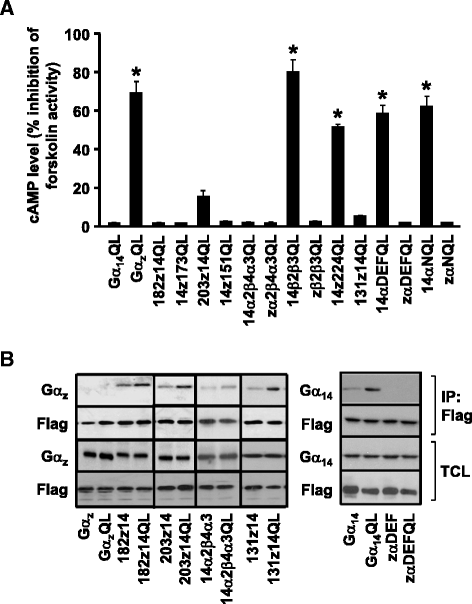
Results: Four chimeras with the core PLCβ-interacting residues composed of Gαz sequences were capable of binding PLCβ2 and stimulating the formation of inositol trisphosphate. Surprisingly, all chimeras with a Gαz N-terminal half failed to functionally associate with PLCβ2, despite the fact that many of them contained the core PLCβ-interacting residues from Gα14. Further analyses revealed that the non-PLCβ2 interacting chimeras were capable of interacting with other effector molecules such as adenylyl cyclase and tetratricopeptide repeat 1, indicating that they could adopt a GTP-bound active conformation.
Conclusion: Collectively, our study suggests that the previously identified PLCβ-interacting residues are insufficient to ensure productive interaction of Gα14 with PLCβ, while an intact N-terminal half of Gα14 is apparently required for PLCβ interaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of activated Gαq to the tumor suppressor Fhit is enhanced by phospholipase Cβ.BMC Cancer. 2015 Oct 24;15:775. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1802-z. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26497576 Free PMC article.
-
Gα16 interacts with tetratricopeptide repeat 1 (TPR1) through its β3 region to activate Ras independently of phospholipase Cβ signaling.BMC Struct Biol. 2011 Apr 13;11:17. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-11-17. BMC Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21486497 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase Cβ connects G protein signaling with RNA interference.Adv Biol Regul. 2016 May;61:51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2015.11.006. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Adv Biol Regul. 2016. PMID: 26746047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gαq and the Phospholipase Cβ3 X-Y Linker Regulate Adsorption and Activity on Compressed Lipid Monolayers.Biochemistry. 2019 Aug 13;58(32):3454-3467. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00441. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31322863 Free PMC article.
-
Gαq signalling: the new and the old.Cell Signal. 2014 May;26(5):833-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24440667 Review.
Cited by
-
The Conformational Dynamics of Heterotrimeric G Proteins During GPCR-Mediated Activation.Subcell Biochem. 2022;99:271-284. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-00793-4_8. Subcell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36151379 Review.
References
-
- Jhon DY, Lee HH, Park D, Lee CW, Lee KH, Yoo OJ, et al. Cloning, sequencing, purification, and Gq-dependent activation of phospholipase C-beta 3. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(9):6654–6661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

