Inhibition of NOX2 reduces locomotor impairment, inflammation, and oxidative stress after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 26377802
- PMCID: PMC4574142
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-015-0391-8
Inhibition of NOX2 reduces locomotor impairment, inflammation, and oxidative stress after spinal cord injury
Abstract
Background: Spinal cord injury (SCI) results in the activation of the NADPH oxidase (NOX) enzyme, inducing production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). We hypothesized that the NOX2 isoform plays an integral role in post-SCI inflammation and functional deficits.
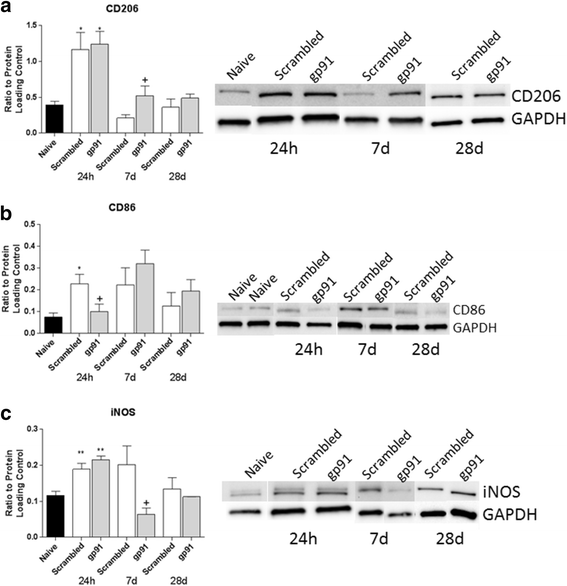
Methods: Moderate spinal cord contusion injury was performed in adult male mice, and flow cytometry, western blot, and immunohistochemistry were used to assess NOX2 activity and expression, inflammation, and M1/M2 microglia/macrophage polarization from 1 to 28 days after injury. The NOX2-specific inhibitor, gp91ds-tat, was injected into the intrathecal space immediately after impact. The Basso Mouse Scale (BMS) was used to assess locomotor function at 24 h post-injury and weekly thereafter.
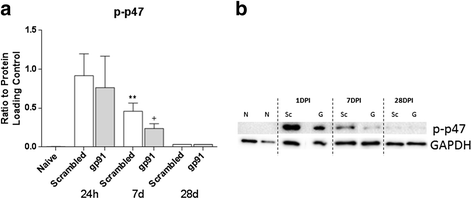
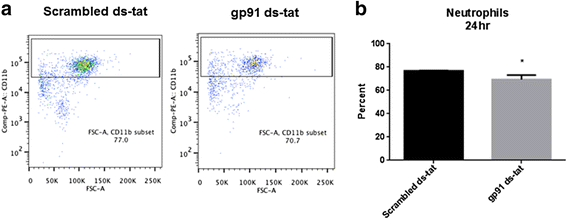
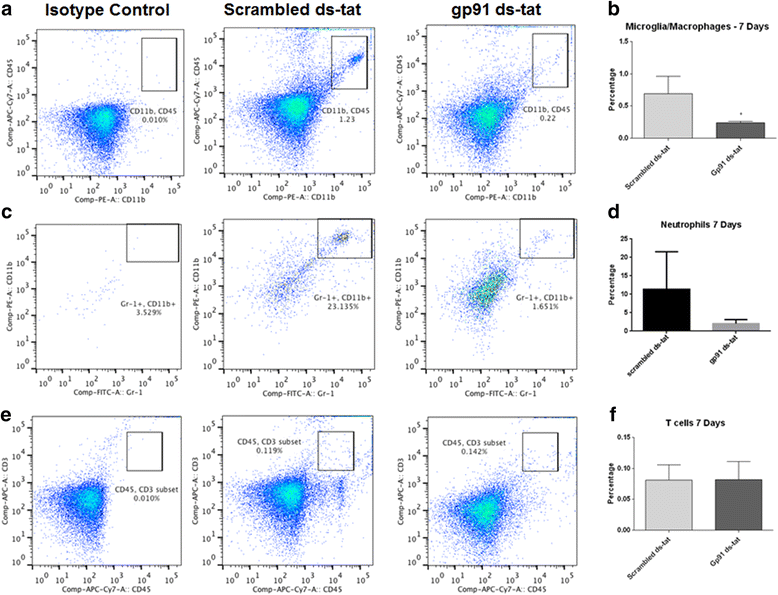
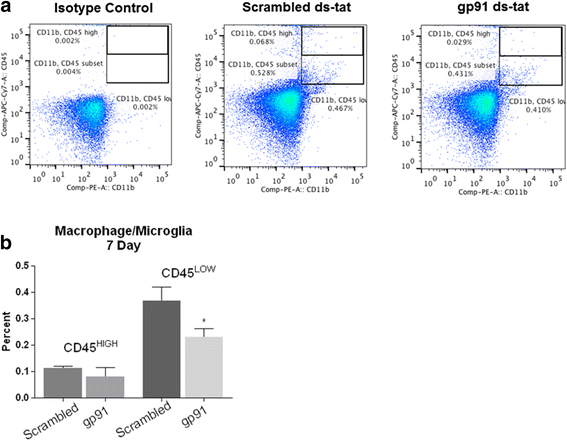
Results: Our findings show that gp91ds-tat treatment significantly improved functional recovery through 28 days post-injury and reduced inflammatory cell concentrations in the injured spinal cord at 24 h and 7 days post-injury. In addition, a number of oxidative stress markers were reduced in expression at 24 h after gp91ds-tat treatment, which was accompanied by a reduction in M1 polarization marker expression.
Conclusion: Based on our findings, we now conclude that inhibition of NOX2 significantly improves outcome after SCI, most likely via acute reductions in oxidative stress and inflammation. NOX2 inhibition may therefore have true potential as a therapy after SCI.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NADPH oxidase isoform expression is temporally regulated and may contribute to microglial/macrophage polarization after spinal cord injury.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2016 Dec;77:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27729244 Free PMC article.
-
Age exacerbates microglial activation, oxidative stress, inflammatory and NOX2 gene expression, and delays functional recovery in a middle-aged rodent model of spinal cord injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Aug 18;14(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0933-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28821269 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide preconditioning facilitates M2 activation of resident microglia after spinal cord injury.J Neurosci Res. 2014 Dec;92(12):1647-58. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23448. Epub 2014 Jul 10. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 25044014
-
NOX2-dependent regulation of inflammation.Clin Sci (Lond). 2016 Apr 1;130(7):479-90. doi: 10.1042/CS20150660. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26888560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central Nervous System Injury and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase: Oxidative Stress and Therapeutic Targets.J Neurotrauma. 2017 Feb 15;34(4):755-764. doi: 10.1089/neu.2016.4486. Epub 2016 Jun 27. J Neurotrauma. 2017. PMID: 27267366 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Small Molecules To Treat Seizures and Epilepsy: From Bench to Bedside.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Jun;37(6):463-484. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27062228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 14 promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury through regulating microglia M1/M2 polarization via STAT1/6 pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Aug;18(8):1809-1817. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.357909. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36751810 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs): A Novel Class of Neuroprotective Agents With a Multimodal Mechanism of Action.Front Neurol. 2020 Feb 25;11:108. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00108. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32158425 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Microglial Hv1 as a Target for Immunomodulation in Myelin Repair.Aging Dis. 2024 May 7;15(3):1176-1203. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1107. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38029392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of NOX2 signaling limits pain-related behavior and improves motor function in male mice after spinal cord injury: Participation of IL-10/miR-155 pathways.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Aug;80:73-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.02.024. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 30807841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kigerl KA, Gensel JC, Ankeny DP, Alexander JK, Donnelly DJ, Popovich PG. Identification of two distinct macrophage subsets with divergent effects causing either neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2009;29:13435–44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3257-09.2009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

