Ultrastructure and lipid composition of detergent-resistant membranes derived from mammalian sperm and two types of epithelial cells
- PMID: 26378009
- PMCID: PMC4700079
- DOI: 10.1007/s00441-015-2272-y
Ultrastructure and lipid composition of detergent-resistant membranes derived from mammalian sperm and two types of epithelial cells
Abstract
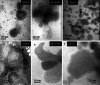
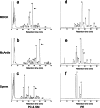
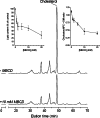
Lipid rafts are micro-domains of ordered lipids (Lo phase) in biological membranes. The Lo phase of cellular membranes can be isolated from disordered lipids (Ld phase) after treatment with 1 % Triton X-100 at 4 °C in which the Lo phase forms the detergent-resistant membrane (DRM) fraction. The lipid composition of DRM derived from Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells, McArdle cells and porcine sperm is compared with that of the whole cell. Remarkably, the unsaturation and chain length degree of aliphatic chains attached to phospholipids is virtually the same between DRM and whole cells. Cholesterol and sphingomyelin were enriched in DRMs but to a cell-specific molar ratio. Sulfatides (sphingolipids from MDCK cells) were enriched in the DRM while a seminolipid (an alkylacylglycerolipid from sperm) was depleted from the DRM. Treatment with <5 mM methyl-ß-cyclodextrin (MBCD) caused cholesterol removal from the DRM without affecting the composition and amount of the phospholipid while higher levels disrupted the DRM. The substantial amount of (poly)unsaturated phospholipids in DRMs as well as a low stoichiometric amount of cholesterol suggest that lipid rafts in biological membranes are more fluid and dynamic than previously anticipated. Using negative staining, ultrastructural features of DRM were monitored and in all three cell types the DRMs appeared as multi-lamellar vesicular structures with a similar morphology. The detergent resistance is a result of protein-cholesterol and sphingolipid interactions allowing a relatively passive attraction of phospholipids to maintain the Lo phase. For this special issue, the relevance of our findings is discussed in a sperm physiological context.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Detergent-resistant membranes; Epithelial cell; Glycolipids; Lipid rafts; Phospholipids; Sperm; Ultrastructure.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipids that determine detergent resistance of MDCK cell membrane fractions.Chem Phys Lipids. 2015 Oct;191:68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Chem Phys Lipids. 2015. PMID: 26320877
-
The isolation and structure of membrane lipid rafts from rat brain.Biochimie. 2007 Feb;89(2):192-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2006.07.006. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Biochimie. 2007. PMID: 16935406
-
Sphingomyelin and cholesterol: from membrane biophysics and rafts to potential medical applications.Subcell Biochem. 2004;37:167-215. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-5806-1_5. Subcell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15376621 Review.
-
Lipid composition of membrane rafts, isolated with and without detergent, from the spleen of a mouse model of Gaucher disease.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Dec 6;442(1-2):62-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.009. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 24220330
-
A lipid matrix model of membrane raft structure.Prog Lipid Res. 2010 Oct;49(4):390-406. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2010.05.002. Epub 2010 May 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20478335 Review.
Cited by
-
Sperm lipidic profiles differ significantly between ejaculates resulting in pregnancy or not following intracytoplasmic sperm injection.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018 Nov;35(11):1973-1985. doi: 10.1007/s10815-018-1284-4. Epub 2018 Aug 14. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018. PMID: 30105539 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the reproductive tract in modifications of the sperm membrane surface.J Reprod Dev. 2016 Aug 25;62(4):337-43. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2016-028. Epub 2016 Mar 24. J Reprod Dev. 2016. PMID: 27009019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-algal activity of the 12-5-12 gemini surfactant results from its impact on the photosynthetic apparatus.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 27;11(1):2360. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82165-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33504917 Free PMC article.
-
Detergent Resistant Membrane Domains in Broccoli Plasma Membrane Associated to the Response to Salinity Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 17;21(20):7694. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207694. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33080920 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Screening of Lipidomic Adaptations in Cultured Cells.Biomolecules. 2019 Jan 24;9(2):42. doi: 10.3390/biom9020042. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30682837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed SN, Brown DA, London E. On the origin of sphingolipid/cholesterol-rich detergent-insoluble cell membranes: physiological concentrations of cholesterol and sphingolipid induce formation of a detergent-insoluble, liquid-ordered lipid phase in model membranes. Biochemistry. 1997;36:10944–10953. doi: 10.1021/bi971167g. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

