Orchestration of ErbB3 signaling through heterointeractions and homointeractions
- PMID: 26378253
- PMCID: PMC4710241
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-06-1114
Orchestration of ErbB3 signaling through heterointeractions and homointeractions
Erratum in
-
Correction.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Feb 15;27(4):731. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26869179 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
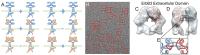
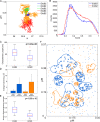
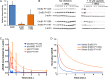
Members of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases are capable of both homointeractions and heterointeractions. Because each receptor has a unique set of binding sites for downstream signaling partners and differential catalytic activity, subtle shifts in their combinatorial interplay may have a large effect on signaling outcomes. The overexpression and mutation of ErbB family members are common in numerous human cancers and shift the balance of activation within the signaling network. Here we report the development of a spatial stochastic model that addresses the dynamics of ErbB3 homodimerization and heterodimerization with ErbB2. The model is based on experimental measures for diffusion, dimer off-rates, kinase activity, and dephosphorylation. We also report computational analysis of ErbB3 mutations, generating the prediction that activating mutations in the intracellular and extracellular domains may be subdivided into classes with distinct underlying mechanisms. We show experimental evidence for an ErbB3 gain-of-function point mutation located in the C-lobe asymmetric dimerization interface, which shows enhanced phosphorylation at low ligand dose associated with increased kinase activity.
© 2015 McCabe Pryor, Steinkamp, et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures





References
-
- Andrews SS, Bray D. Stochastic simulation of chemical reactions with spatial resolution and single molecule detail. Phys Biol. 2004;1:137–151. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Swain SM. Novel anticancer targets: revisiting ErbB2 and discovering ErbB3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:463–475. - PubMed
-
- Blinov ML, Faeder JR, Goldstein B, Hlavacek WS. A network model of early events in epidermal growth factor receptor signaling that accounts for combinatorial complexity. Biosystems. 2006;83:136–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

