Ghrelin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis through Regulation of TGF-β1 Expression and Autophagy
- PMID: 26378522
- PMCID: PMC4613288
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160921911
Ghrelin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis through Regulation of TGF-β1 Expression and Autophagy
Abstract
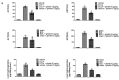
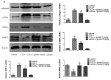
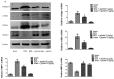
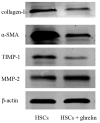
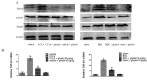
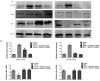
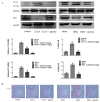
Ghrelin is a stomach-derived growth hormone secretagogue that promotes various physiological effects, including energy metabolism and amelioration of inflammation. The purpose of this study was to investigate the protective mechanism of ghrelin against liver fibrosis. Liver fibrosis was induced in C57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal injection of CCl₄ (2.0 mL/kg of 10% CCl₄ v/v solution in peanut oil) two times per week for eight weeks. Ghrelin (10 μg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected two times per week for eight weeks. A second murine liver fibrosis model was induced by bile duct ligation (BDL) and concurrent ghrelin administration for four weeks. Hematoxylin eosin (H&E), and Masson's trichrome were used to detect pathological changes to liver tissue. Western blotting was used to detect protein levels of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, phosphorylated Smad3 (p-Smad3), I-collage, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) 2, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) 1, phosphorylated NF-κB (p-NF-κB), and microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3). In addition, qRT-PCR was used to detect mRNA levels of TGF-β1, I-collage, α-SMA, MMP2, TIMP1 and LC3, while levels of TGF-β1, p-Smad3, I-collage, α-SMA, and LC3 were detected immunohistochemically. Levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase were significantly decreased by ghrelin treatment. Ghrelin administration also significantly reduced the extent of pathological changes in both murine liver fibrosis models. Expression levels of I-collage and α-SMA in both models were clearly reduced by ghrelin administration. Furthermore, ghrelin treatment decreased protein expression of TGF-β1 and p-Smad3. The protein levels of NF-κB and LC3 were increased in the CCl₄- and BDL-treatment groups but were significantly reduced following ghrelin treatment. In addition, ghrelin inhibited extracellular matrix formation by decreasing NF-κB expression and maintaining the balance between MMP2 and TIMP1. Our results demonstrated that ghrelin attenuates liver fibrosis via inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways, as well as autophagy suppression.
Keywords: CCl4; NF-κB; TGF-β1-Smad; autophagy; bile duct ligation; fibrosis; ghrelin; hepatic stellate cells.
Figures




References
-
- Friedman S.L. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis—Mechanisms and treatment strategies. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;328:1828–1835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

