Pandemrix™ and narcolepsy: A critical appraisal of the observational studies
- PMID: 26379011
- PMCID: PMC4962758
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1068486
Pandemrix™ and narcolepsy: A critical appraisal of the observational studies
Abstract
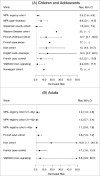
A link between Pandemrix™ (AS03-adjuvanted H1N1 pandemic influenza vaccine, GSK Vaccines, Belgium) and narcolepsy was first suspected in 2010 in Sweden and Finland following a number of reports in children and adolescents. Initial scepticism about the reported association faded as additional countries reported similar findings, leading several regulatory authorities to restrict the use of Pandemrix™. The authors acknowledge that currently available data suggest an increased risk of narcolepsy following vaccination with Pandemrix™; however, from an epidemiologist's perspective, significant methodological limitations of the studies have not been fully addressed and raise questions about the reported risk estimates. We review the most important biases and confounders that potentially occurred in 12 European studies of the observed association between Pandemrix™ and narcolepsy, and call for further analyses and debate.
Keywords: epidemiological bias, H1N1, influenza, narcolepsy, vaccine.
Figures
References
-
- Mereckiene J, Cotter S, Weber J, Nicoll A, D'Ancona F, Lopalco P. Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 vaccination policies and coverage in Europe. Euro Surveill 2012; 17(4):20064. - PubMed
-
- Mereckiene J, Cotter S, Nicoll A, Lopalco P, Noori T, Weber J, D'Ancona F, Levy-Bruhl D, Dematte L, Giambi C, et al.. Seasonal influenza immunisation in Europe. Overview of recommendations and vaccination coverage for three seasons: pre-pandemic (2008/09), pandemic (2009/10) and post-pandemic (2010/11). Euro Surveill 2014; 19:20780; PMID:24786262 - PubMed
-
- ECDC. European centre for disease prevention and control Narcolepsy in association with pandemic influenza vaccination. A multi-country European epidemiological investigation Stockholm, September 2012. Available at http://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/Vaesco%20report%2...
-
- Läkemedelsverket. Medical Products Agency The MPA investigates reports of narcolepsy in patients vaccinated with Pandemrix, 2010. Available at: http://www.lakemedelsverket.se/english/All-news/NYHETER-2010/The-MPA-inv...
-
- Läkemedelsverket. Medical Products Agency Occurrence of narcolepsy with cataplexy among children and adolescents in relation to the H1N1 pandemic and Pandemrix vaccinations ‐ Results of a case inventory study by the MPA in Sweden during 2009 ‐ 2010. Report no. 1. Sweden: 2011:1-20. Available at http://www.lakemedelsverket.se/upload/nyheter/2011/Fallinventeringsrappo...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous