Biochemical Markers of Physical Exercise on Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: Systematic Review and Perspectives
- PMID: 26379621
- PMCID: PMC4549649
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00187
Biochemical Markers of Physical Exercise on Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: Systematic Review and Perspectives
Abstract
Background: The cognitive effects of physical exercise in patients with dementia disorders or mild cognitive impairment have been examined in various studies; however the biochemical effects of exercise from intervention studies are largely unknown. The objective of this systematic review is to investigate the published results on biomarkers in physical exercise intervention studies in patients with MCI or dementia.
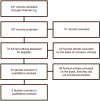
Methods: The PubMed database was searched for studies from 1976 to February 2015. We included intervention studies investigating the effect of physical exercise activity on biomarkers in patients with MCI or dementia.
Results: A total of eight studies were identified (n = 447 patients) evaluating exercise regimes with variable duration (single session-three sessions/week for 26 weeks) and intensity (light-resistance training-high-intensity aerobic exercise). Various biomarkers were measured before and after intervention. Seven of the eight studies found a significant effect on their selected biomarkers with a positive effect of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, cholesterol, testosterone, estradiol, dehydroepiadrosterone, and insulin in the intervention groups compared with controls.
Conclusion: Although few studies suggest a beneficial effect on selected biomarkers, we need more knowledge of the biochemical effect of physical exercise in dementia or MCI.
Keywords: MCI; biomarkers; dementia; exercise intervention; physical activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Exercise on Inflammatory, Oxidative, and Neurotrophic Biomarkers on Cognitively Impaired Individuals Diagnosed With Dementia or Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2019 Apr 23;74(5):616-624. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gly173. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30084942
-
Physical exercise increases peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factors in patients with cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis.Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2021;39(3):159-171. doi: 10.3233/RNN-201060. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33998558
-
Physical exercise attenuates cognitive decline and reduces behavioural problems in people with mild cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review.J Physiother. 2020 Jan;66(1):9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2019.11.014. Epub 2019 Dec 13. J Physiother. 2020. PMID: 31843427
-
Exercise Training for Mild Cognitive Impairment Adults Older Than 60: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;88(4):1263-1278. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220243. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 35811527 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of physical activities on dementia-related biomarkers: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2021 Jan 20;6(1):e12109. doi: 10.1002/trc2.12109. eCollection 2020. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2021. PMID: 33521235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between housework and the risk of dementia among older Chinese adults: a prospective cohort study.Front Psychol. 2023 Jul 24;14:1228059. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1228059. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37554140 Free PMC article.
-
Biological effects of dosing aerobic exercise and neuromuscular electrical stimulation in rats.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 7;7(1):10830. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11260-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28883534 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Neuroinflammation to Treat Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Drugs. 2017 Dec;31(12):1057-1082. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0483-3. CNS Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29260466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study Protocol on Hormonal Mediation of Exercise on Cognition, Stress and Immunity (PRO-HMECSI): Effects of Different Exercise Programmes in Institutionalized Elders.Front Public Health. 2016 Jun 27;4:133. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2016.00133. eCollection 2016. Front Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27446898 Free PMC article.
-
Association of cognitive performance with overall, dosage, intensity, and domain physical activity in aging: NHANES 2011-2014.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Nov 5;24(1):910. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05503-2. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39501194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. Policy Brief for Heads of Government: The Global Impact of Dementia. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International (2013). p. 2013–50.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources