The PFP and ESG protein function prediction methods in 2014: effect of database updates and ensemble approaches
- PMID: 26380077
- PMCID: PMC4570625
- DOI: 10.1186/s13742-015-0083-4
The PFP and ESG protein function prediction methods in 2014: effect of database updates and ensemble approaches
Abstract
Background: Functional annotation of novel proteins is one of the central problems in bioinformatics. With the ever-increasing development of genome sequencing technologies, more and more sequence information is becoming available to analyze and annotate. To achieve fast and automatic function annotation, many computational (automated) function prediction (AFP) methods have been developed. To objectively evaluate the performance of such methods on a large scale, community-wide assessment experiments have been conducted. The second round of the Critical Assessment of Function Annotation (CAFA) experiment was held in 2013-2014. Evaluation of participating groups was reported in a special interest group meeting at the Intelligent Systems in Molecular Biology (ISMB) conference in Boston in 2014. Our group participated in both CAFA1 and CAFA2 using multiple, in-house AFP methods. Here, we report benchmark results of our methods obtained in the course of preparation for CAFA2 prior to submitting function predictions for CAFA2 targets.
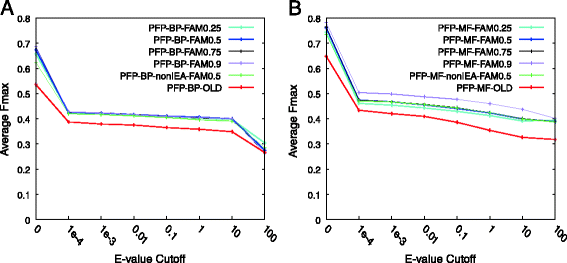
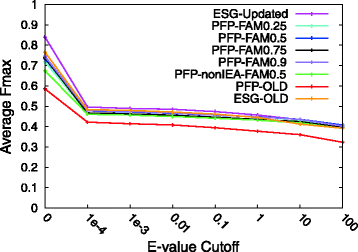
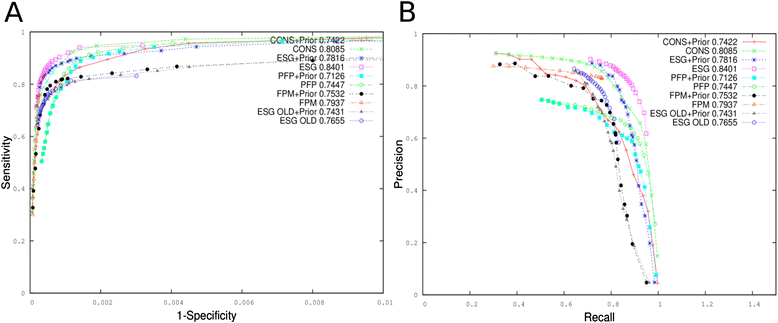
Results: For CAFA2, we updated the annotation databases used by our methods, protein function prediction (PFP) and extended similarity group (ESG), and benchmarked their function prediction performances using the original (older) and updated databases. Performance evaluation for PFP with different settings and ESG are discussed. We also developed two ensemble methods that combine function predictions from six independent, sequence-based AFP methods. We further analyzed the performances of our prediction methods by enriching the predictions with prior distribution of gene ontology (GO) terms. Examples of predictions by the ensemble methods are discussed.
Conclusions: Updating the annotation database was successful, improving the Fmax prediction accuracy score for both PFP and ESG. Adding the prior distribution of GO terms did not make much improvement. Both of the ensemble methods we developed improved the average Fmax score over all individual component methods except for ESG. Our benchmark results will not only complement the overall assessment that will be done by the CAFA organizers, but also help elucidate the predictive powers of sequence-based function prediction methods in general.
Keywords: CAFA; ESG; PFP; Protein function; consensus method; ensemble method; function prediction; gene annotation; sequence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In-depth performance evaluation of PFP and ESG sequence-based function prediction methods in CAFA 2011 experiment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S3-S2. Epub 2013 Feb 28. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23514353 Free PMC article.
-
Using PFP and ESG Protein Function Prediction Web Servers.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1611:1-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7015-5_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28451967
-
PFP/ESG: automated protein function prediction servers enhanced with Gene Ontology visualization tool.Bioinformatics. 2015 Jan 15;31(2):271-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu646. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25273111 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Ontology annotation of the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Feb 19;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-S1-S8. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19278556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond annotation transfer by homology: novel protein-function prediction methods to assist drug discovery.Drug Discov Today. 2005 Nov 1;10(21):1475-82. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03621-4. Drug Discov Today. 2005. PMID: 16243268 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Situation with Recombinant Toxins: Diversity, Production and Application Purposes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 27;24(5):4630. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054630. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
INGA 2.0: improving protein function prediction for the dark proteome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W373-W378. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz375. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31073595 Free PMC article.
-
ContactPFP: Protein function prediction using predicted contact information.Front Bioinform. 2022 Jun;2:896295. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2022.896295. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Front Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35875419 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling of hydatid fluid from pulmonary cystic echinococcosis.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Mar 21;15(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05232-8. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35313982 Free PMC article.
-
BUSCA: an integrative web server to predict subcellular localization of proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 2;46(W1):W459-W466. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky320. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29718411 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

