Intrathecal trastuzumab: immunotherapy improves the prognosis of leptomeningeal metastases in HER-2+ breast cancer patient
- PMID: 26380087
- PMCID: PMC4570757
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-015-0084-y
Intrathecal trastuzumab: immunotherapy improves the prognosis of leptomeningeal metastases in HER-2+ breast cancer patient
Abstract
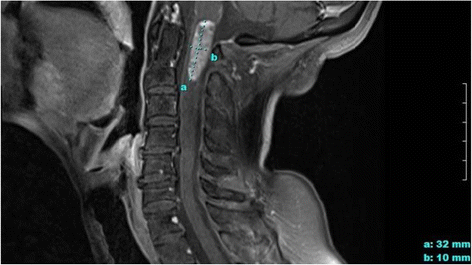
We describe the clinical and therapeutic course of a 51-year-old woman with HER-2+ breast cancer who developed leptomeningeal (LM) and spinal cord metastases after 8 years of stable disease on combination therapy with intravenous (IV) trastuzumab. Due to progressive CNS disease, intrathecal (IT) trastuzumab was introduced to enhance HER-2+ therapy into the CSF space. A combination HER-2+ targeted approach achieved clinical remission with stable disease in our patient 46 months after she was diagnosed with LM metastases. However, spinal cord C-1 metastasis was not fully controlled with IT trastuzumab, ultimately leading to the patient's respiratory compromise. In our patient, IT trastuzumab immunotherapy improved prognosis and was an effective strategy to manage HER-2+ LM disease. Given alone or alongside other anti-HER-2+ therapeutics with sufficient CNS penetration, IT trastuzumab could extend the lifespan of patients with leptomeningeal and CNS metastases.
Keywords: Antibody mediated immunotherapy; HER-2+ leptomeningeal CNS metastases; Intrathecal trastuzumab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sanctuary site leptomeningeal metastases in HER-2 positive breast cancer: A review in the era of trastuzumab.Breast. 2016 Apr;26:54-8. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2015.11.005. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Breast. 2016. PMID: 27017242 Review.
-
Central nervous system metastases in women who receive trastuzumab-based therapy for metastatic breast carcinoma.Cancer. 2003 Jun 15;97(12):2972-7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11436. Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12784331
-
Therapy of leptomeningeal metastasis in solid tumors.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Feb;43:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 26827696 Review.
-
Prolonged Response and Restoration of Functional Independence with Bevacizumab plus Vinorelbine as Third-Line Treatment for Breast Cancer-Related Leptomeningeal Metastases.Case Rep Oncol. 2015 Feb 12;8(1):72-7. doi: 10.1159/000375293. eCollection 2015 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25848355 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal trastuzumab (Herceptin) and methotrexate for meningeal carcinomatosis in HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: a case report.Anticancer Drugs. 2008 Sep;19(8):832-6. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32830b58b0. Anticancer Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18690096
Cited by
-
Breast leptomeningeal disease: a review of current practices and updates on management.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Sep;177(2):277-294. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05317-6. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31209686 Review.
-
Recurrent Meningitis.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017 Jul;21(7):33. doi: 10.1007/s11916-017-0635-7. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017. PMID: 28551737 Review.
-
Leptomeningeal disease: current diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 16;8(42):73312-73328. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20272. eCollection 2017 Sep 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29069871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addressing BBB Heterogeneity: A New Paradigm for Drug Delivery to Brain Tumors.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Dec 11;12(12):1205. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12121205. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33322488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic Modeling of Intrathecal Chemotherapy Pharmacokinetics in the Human Central Nervous System.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 1;30(7):1397-1408. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3062. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38289997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244(4905):707-12. - PubMed
-
- Bendell JC, Domchek SM, Burstein HJ, Harris L, Younger J, Kuter I, et al. Central nervous system metastases in women who receive trastuzumab-based therapy for metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;97(12):2972-7. - PubMed
-
- Vogel CL, Cobleigh MA, Tripathy D, Gutheil JC, Harris LN, Fehrenbacher L, et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2002;20(3):719-26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous