Vascular and plaque imaging with ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide
- PMID: 26381872
- PMCID: PMC4574723
- DOI: 10.1186/s12968-015-0183-4
Vascular and plaque imaging with ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide
Abstract
Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) has become a primary tool for non-invasive assessment of cardiovascular anatomy, pathology and function. Existing contrast agents have been utilised for the identification of infarction, fibrosis, perfusion deficits and for angiography. Novel ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide (USPIO) contrast agents that are taken up by inflammatory cells can detect cellular inflammation non-invasively using CMR, potentially aiding the diagnosis of inflammatory medical conditions, guiding their treatment and giving insight into their pathophysiology. In this review we describe the utilization of USPIO as a novel contrast agent in vascular disease.
Figures
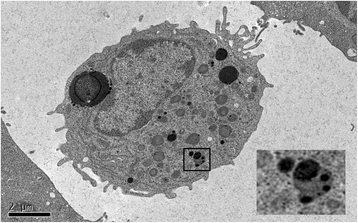
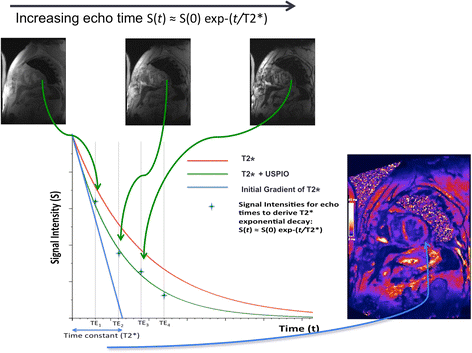
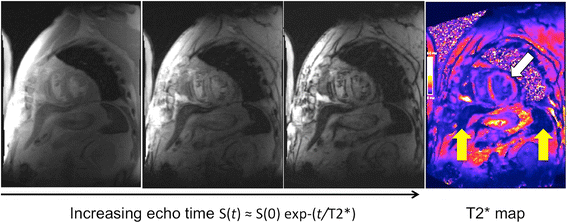
References
-
- Schelbert EB, Hsu LY, Anderson SA, Mohanty BD, Karim SM, Kellman P, et al. Late gadolinium-enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance identifies postinfarction myocardial fibrosis and the border zone at the near cellular level in ex vivo rat heart. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;3:743–52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.108.835793. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schiller B, Bhat P, Sharma A, Li Z, Fortin G, McLaughlin J, et al. Safety of Feraheme¬Æ(Ferumoxytol) in hemodialysis patients at 3 dialysis chains over a 1-year period. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:477A–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

