Zinc and diabetes mellitus: understanding molecular mechanisms and clinical implications
- PMID: 26381880
- PMCID: PMC4573932
- DOI: 10.1186/s40199-015-0127-4
Zinc and diabetes mellitus: understanding molecular mechanisms and clinical implications
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Studies have shown that Zinc has numerous beneficial effects in both type-1 and type-2 diabetes. We aim to evaluate the literature on the mechanisms and molecular level effects of Zinc on glycaemic control, β-cell function, pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications.
Methods: A review of published studies reporting mechanisms of action of Zinc in diabetes was undertaken in PubMed and SciVerse Scopus medical databases using the following search terms in article title, abstract or keywords; ("Zinc" or "Zn") and ("mechanism" or "mechanism of action" or "action" or "effect" or "pathogenesis" or "pathology" or "physiology" or "metabolism") and ("diabetes" or "prediabetes" or "sugar" or "glucose" or "insulin").
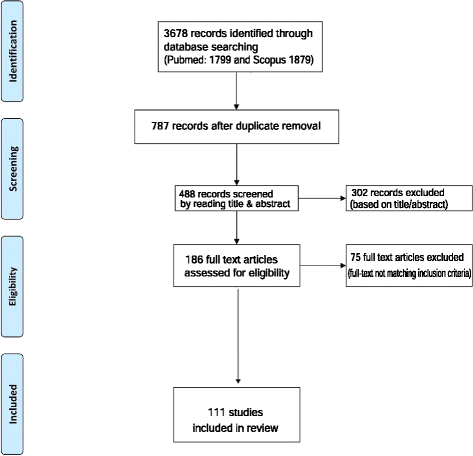
Results: The literature search identified the following number of articles in the two databases; PubMed (n = 1799) and SciVerse Scopus (n = 1879). After removing duplicates the total number of articles included in the present review is 111. Our results show that Zinc plays an important role in β-cell function, insulin action, glucose homeostasis and the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications.
Conclusion: Numerous in-vitro and in-vivo studies have shown that Zinc has beneficial effects in both type-1 and type-2 diabetes. However further randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trials conducted for an adequate duration, are required to establish therapeutic safety in humans.
Similar articles
-
The Role of Zinc and Copper in Insulin Resistance and Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(39):6643-6657. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190902122155. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31475889 Review.
-
Anti-hyperglycemic Effect of Long-Term Bis(hinokitiolato)zinc Complex ([Zn(hkt)2]) Ingestion on Insulin Resistance and Pancreatic Islet Cells Protection in Type 2 Diabetic KK-Ay Mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(3):318-326. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b16-00797. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28250273
-
Effects of zinc supplementation on diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012 Apr 19;4(1):13. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-4-13. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012. PMID: 22515411 Free PMC article.
-
Insulino-mimetic and anti-diabetic effects of zinc.J Inorg Biochem. 2013 Mar;120:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.11.006. Epub 2012 Dec 3. J Inorg Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23266931 Review.
-
Leucas cephalotes regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and improves antioxidant status in IDDM and NIDDM rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Jan 8;127(1):98-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.09.042. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19799987
Cited by
-
Imaging Tissue Physiology In Vivo by Use of Metal Ion-Responsive MRI Contrast Agents.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Sep 24;13(10):268. doi: 10.3390/ph13100268. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32987721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress as the Main Target in Diabetic Retinopathy Pathophysiology.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Aug 14;2019:8562408. doi: 10.1155/2019/8562408. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31511825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc Intake and Status and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2019 May 8;11(5):1027. doi: 10.3390/nu11051027. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31071930 Free PMC article.
-
Leptadenia hastata Leaf Extract ameliorates oxidative stress and serum biochemical parameters in Streptozotocin-Induced diabetes in Wistar rats.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Aug 3;21(2):1273-1281. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01017-z. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 36404850 Free PMC article.
-
The Crossroads between Zinc and Steroidal Implant-Induced Growth of Beef Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jun 27;11(7):1914. doi: 10.3390/ani11071914. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas - The Economic Impacts of Diabetes. [http://www.diabetesatlas.com/content/economic-impacts-diabetes]
-
- WHO Diabetes Fact Sheet. [http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/index.html]
-
- Diabetes: the cost of diabetes [http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs236/en/]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical