Enhanced EJ Cell Killing of (125)I Radiation by Combining with Cytosine Deaminase Gene Therapy Regulated by Synthetic Radio-Responsive Promoter
- PMID: 26382009
- PMCID: PMC4601673
- DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2015.1862
Enhanced EJ Cell Killing of (125)I Radiation by Combining with Cytosine Deaminase Gene Therapy Regulated by Synthetic Radio-Responsive Promoter
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the enhancing effect of radionuclide therapy by the therapeutic gene placed under the control of radio-responsive promoter.
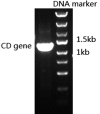
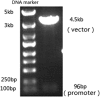
Methods: The recombinant lentivirus E8-codA-GFP, including a synthetic radiation-sensitive promoter E8, cytosine deaminase (CD) gene, and green fluorescent protein gene, was constructed. The gene expression activated by (125)I radiation was assessed by observation of green fluorescence. The ability of converting 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC) to 5-fluorourial (5-FU) by CD enzyme was assessed by high-performance liquid chromatography. The viability of the infected cells exposed to (125)I in the presence of 5-FC was determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, and the infected cells exposed to (125)I alone served as negative control and 5-FU as positive control.
Results: The recombinant lentiviral vector was constructed successfully. On exposure of infected cells to (125)I, green fluorescence can be observed and 5-FU can be detected. MTT assay showed that the survival rate for infected cells treated with (125)I was lower compared with the (125)I control group, but higher than the positive control group.
Conclusion: The synthetic promoter E8 can induce the expression of downstream CD gene under (125)I radiation, and the tumor killing effect of (125)I can be enhanced by combining CD gene therapy with radiosensitive promoter.
Keywords: 125I; 5-fluorocytosine; cytosine deaminase; radiation-sensitive promoter; recombinant lentivirus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular chemotherapy combined with radiation therapy enhances killing of cholangiocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Res. 1997 Oct 1;57(19):4325-32. Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9331094
-
Antitumor efficiency of the cytosine deaminase/5-fluorocytosine suicide gene therapy system on malignant gliomas: an in vivo study.Med Sci Monit. 2009 Jan;15(1):BR13-20. Med Sci Monit. 2009. PMID: 19114960
-
Cytosine deaminase-producing human mesenchymal stem cells mediate an antitumor effect in a mouse xenograft model.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Aug;24(8):1393-400. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05862.x. Epub 2009 May 28. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19486256
-
Management of malignant pleural effusion by suicide gene therapy in advanced stage lung cancer: a case series and literature review.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012 Sep;19(9):593-600. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.36. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22744209 Review.
-
Escherichia coli cytosine deaminase: Structural and biotechnological aspects.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2024 Feb;71(1):5-16. doi: 10.1002/bab.2516. Epub 2023 Sep 24. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37743549 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced tumor inhibiting effect of 131I-BDI-1-based radioimmunotherapy and cytosine deaminase gene therapy modulated by a radio-sensitive promoter in nude mice bearing bladder cancer.J Radiat Res. 2023 Jan 20;64(1):85-90. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrac075. J Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 36418230 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of iodinated quorum sensing peptides by LC-UV/ESI ion trap mass spectrometry.J Pharm Anal. 2018 Feb;8(1):69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 14. J Pharm Anal. 2018. PMID: 29568670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pool SE, Krenning EP, Koning GA, et al. . Preclinical and clinical studies of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Semin Nucl Med 2010;40:209. - PubMed
-
- Gupta SK, Singla S, Bal C. Renal and hematological toxicity in patients of neuroendocrine tumors after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2012;27:593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
