Tauopathies as clinicopathological entities
- PMID: 26382841
- PMCID: PMC4662611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.09.020
Tauopathies as clinicopathological entities
Abstract
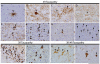
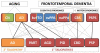
Tauopathies are a class of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by neuronal and/or glial inclusions composed of the microtubule-binding protein, tau. Several lines of evidence suggest tau aggregation is central to the neurodegenerative process in tauopathies. First, recent animal and cell model studies find abnormally-modified tau alone may be transmitted between adjacent neurons and spread to anatomically connected brain regions to recapitulate human disease. Further, staging efforts in human autopsy cases suggest a sequential distribution of tau aggregation in the central nervous system that could reflect this observed cell-to-cell transmission of pathogenic tau species in animal models. Finally, pathogenic mutations in the MAPT gene encoding tau protein cause hereditary forms of tauopathy. Clinically, tauopathies can present with a range of phenotypes that include both movement- and cognitive/behavioral-disorders (i.e. frontotemporal dementia spectrum disorders) or non-specific amnestic symptoms in advanced age. A major limitation is that current clinical diagnostic criteria for these disorders do not reliably differentiate underlying tauopathy from other neurodegenerative diseases, such as TDP-43 proteinopathies. Thus, current research efforts are focused on improving the ante mortem diagnosis of tauopathies, including pre-clinical stages of disease, as many therapeutic strategies for emerging disease-modifying therapies focus on preventing abnormal folding and spread of tau pathology.
Keywords: Argyrophilic grain disease; Corticobasal degeneration; Corticobasal syndrome tauopathy; Frontotemporal dementia; Frontotemporal lobar degeneration; MAPT mutation; Pick's disease; Primary age related tauopathy; Primary progressive aphasia; Progressive supranuclear palsy.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Litvan I, Agid Y, Calne D, Campbell G, Dubois B, Duvoisin RC, et al. Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology. 1996;47:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

