Integrating multi-scale data on homologous recombination into a new recognition mechanism based on simulations of the RecA-ssDNA/dsDNA structure
- PMID: 26384422
- PMCID: PMC4666392
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv883
Integrating multi-scale data on homologous recombination into a new recognition mechanism based on simulations of the RecA-ssDNA/dsDNA structure
Abstract
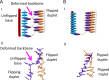
RecA protein is the prototypical recombinase. Members of the recombinase family can accurately repair double strand breaks in DNA. They also provide crucial links between pairs of sister chromatids in eukaryotic meiosis. A very broad outline of how these proteins align homologous sequences and promote DNA strand exchange has long been known, as are the crystal structures of the RecA-DNA pre- and postsynaptic complexes; however, little is known about the homology searching conformations and the details of how DNA in bacterial genomes is rapidly searched until homologous alignment is achieved. By integrating a physical model of recognition to new modeling work based on docking exploration and molecular dynamics simulation, we present a detailed structure/function model of homology recognition that reconciles extremely quick searching with the efficient and stringent formation of stable strand exchange products and which is consistent with a vast body of previously unexplained experimental results.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures






References
-
- Howard-Flanders P., West S.C., Stasiak A. Role of RecA protein spiral filaments in genetic recombination. Nature. 1983;309:215–219. - PubMed
-
- Roca A.I., Cox M.M. The RecA protein: structure and function. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1990;25:415–456. - PubMed
-
- Kowalczykowski S.C., Eggleston A.K. Homologous pairing and DNA strand exchange. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994;63:991–1043. - PubMed
-
- Folta-Stogniew E., O'Malley S., Gupta R.C., Anderson K.S., Radding C.M. Exchange of DNA base pairs that coincides with recognition of homology promoted by E. coli RecA protein. Mol. Cell. 2004;15:965–975. - PubMed
-
- Xiao J., Lee A.M., Singleton S.F. Direct evaluation of a kinetic model for RecA-mediated DNA-strand exchange: The importance of nucleic acid dynamics and entropy during homologous genetic recombination. Chembiochem. 2006;7:1265–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

