NMR analysis of the interaction of picornaviral proteinases Lb and 2A with their substrate eukaryotic initiation factor 4GII
- PMID: 26384734
- PMCID: PMC4815241
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2807
NMR analysis of the interaction of picornaviral proteinases Lb and 2A with their substrate eukaryotic initiation factor 4GII
Abstract
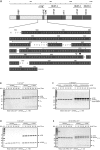
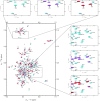
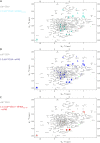
Messenger RNA is recruited to the eukaryotic ribosome by a complex including the eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4E (the cap-binding protein), the scaffold protein eIF4G and the RNA helicase eIF4A. To shut-off host-cell protein synthesis, eIF4G is cleaved during picornaviral infection by a virally encoded proteinase; the structural basis of this reaction and its stimulation by eIF4E is unclear. We have structurally and biochemically investigated the interaction of purified foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) leader proteinase (Lb(pro)), human rhinovirus 2 (HRV2) 2A proteinase (2A(pro)) and coxsackievirus B4 (CVB4) 2A(pro) with purified eIF4GII, eIF4E and the eIF4GII/eIF4E complex. Using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), we completed (13)C/(15) N sequential backbone assignment of human eIF4GII residues 551-745 and examined their binding to murine eIF4E. eIF4GII551-745 is intrinsically unstructured and remains so when bound to eIF4E. NMR and biophysical techniques for determining stoichiometry and binding constants revealed that the papain-like Lb(pro) only forms a stable complex with eIF4GII(551-745) in the presence of eIF4E, with KD values in the low nanomolar range; Lb(pro) contacts both eIF4GII and eIF4E. Furthermore, the unrelated chymotrypsin-like 2A(pro) from HRV2 and CVB4 also build a stable complex with eIF4GII/eIF4E, but with K(D) values in the low micromolar range. The HRV2 enzyme also forms a stable complex with eIF4E; however, none of the proteinases tested complex stably with eIF4GII alone. Thus, these three picornaviral proteinases have independently evolved to establish distinct triangular heterotrimeric protein complexes that may actively target ribosomes involved in mRNA recruitment to ensure efficient host cell shut-off.
Keywords: control of protein synthesis; protein-protein interactions; substrate binding; viral proteases; virus-host interactions.
© 2015 The Authors Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Protein Society.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interaction of 2A proteinase of human rhinovirus genetic group A with eIF4E is required for eIF4G cleavage during infection.Virology. 2017 Nov;511:123-134. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.08.020. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Virology. 2017. PMID: 28843814
-
Recognition of eukaryotic initiation factor 4G isoforms by picornaviral proteinases.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 15;277(46):44300-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208006200. Epub 2002 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12228254
-
Mapping of functional domains in eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) with picornaviral proteases. Implications for cap-dependent and cap-independent translational initiation.J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21975-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21975. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7665619
-
Manipulation of the host translation initiation complex eIF4F by DNA viruses.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Dec;38(6):1511-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0381511. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 21118117 Review.
-
The structures of picornaviral proteinases.Virus Res. 1999 Aug;62(2):159-68. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(99)00043-x. Virus Res. 1999. PMID: 10507325 Review.
Cited by
-
Irreversible inactivation of ISG15 by a viral leader protease enables alternative infection detection strategies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 6;115(10):2371-2376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710617115. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29463763 Free PMC article.
-
4EBP-Dependent Signaling Supports West Nile Virus Growth and Protein Expression.Viruses. 2016 Oct 18;8(10):287. doi: 10.3390/v8100287. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27763553 Free PMC article.
-
Structures and Corresponding Functions of Five Types of Picornaviral 2A Proteins.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 21;8:1373. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01373. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28785248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric activation of RhlB by RNase E induces partial duplex opening in substrate RNA.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Aug 31;10:1139919. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1139919. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37719267 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting distinct proteolytic activities of FMDV Lpro implicates cleavage and degradation of RLR signaling proteins, not its deISGylase/DUB activity, in type I interferon suppression.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jul 15;16(7):e1008702. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008702. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32667958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bovee ML, Marissen WE, Zamora M, Lloyd RE (1998) The predominant elF4G‐specific cleavage activity in poliovirus‐infected HeLa cells is distinct from 2A protease. Virology 245:229–240. - PubMed
-
- Lamphear BJ, Kirchweger R, Skern T, Rhoads RE (1995) Mapping of functional domains in eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) with picornaviral proteases. Implications for cap‐dependent and cap‐independent translational initiation. J Biol Chem 270:21975–21983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

