Neurocognitive functioning and health-related quality of life in patients treated with stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: a prospective study
- PMID: 26385615
- PMCID: PMC4767242
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nov186
Neurocognitive functioning and health-related quality of life in patients treated with stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: a prospective study
Abstract
Background: Stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) is expected to have a less detrimental effect on neurocognitive functioning and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) than whole-brain radiotherapy. To evaluate the impact of brain metastases and SRT on neurocognitive functioning and HRQoL, we performed a prospective study.
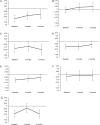
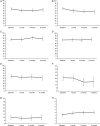
Methods: Neurocognitive functioning and HRQoL of 97 patients with brain metastases were measured before SRT and 1, 3, and 6 months after SRT. Seven cognitive domains were assessed. HRQoL was assessed with the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QLQ-C30 and BN20 questionnaires. Neurocognitive functioning and HRQoL over time were analyzed with linear mixed models and stratified for baseline Karnofsky performance status (KPS), total metastatic volume, and systemic disease.
Results: Median overall survival of patients was 7.7 months. Before SRT, neurocognitive domain and HRQoL scores were lower in patients than in healthy controls. At group level, patients worsened in physical functioning and fatigue at 6 months, while other outcome parameters of HRQoL and cognition remained stable. KPS < 90 and tumor volume >12.6 cm(3) were both associated with worse information processing speed and lower HRQoL scores over 6 months time. Intracranial tumor progression was associated with worsening of executive functioning and motor function.
Conclusions: Prior to SRT, neurocognitive functioning and HRQoL are moderately impaired in patients with brain metastases. Lower baseline KPS and larger tumor volume are associated with worse functioning. Over time, SRT does not have an additional detrimental effect on neurocognitive functioning and HRQoL, suggesting that SRT may be preferred over whole-brain radiotherapy.
Keywords: brain metastases; cognition; health-related quality of life; stereotactic radiotherapy.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Individual changes in neurocognitive functioning and health-related quality of life in patients with brain oligometastases treated with stereotactic radiotherapy.J Neurooncol. 2018 Sep;139(2):359-368. doi: 10.1007/s11060-018-2868-7. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Neurooncol. 2018. PMID: 29663172 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life after whole brain radiotherapy compared with radiosurgery of the tumor bed: results from a randomized trial.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Feb;20(2):150-159. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1703-5. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28616720 Clinical Trial.
-
Health-related quality of life in elderly patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with short-course radiation therapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Jun 1;86(2):285-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.02.013. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23642624 Clinical Trial.
-
Quality of life in patients with primary and metastatic brain cancer as reported in the literature using the EORTC QLQ-BN20 and QLQ-C30.Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2012 Dec;12(6):831-7. doi: 10.1586/erp.12.70. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2012. PMID: 23252363 Review.
-
The EORTC QLQ-BN20 for assessment of quality of life in patients receiving treatment or prophylaxis for brain metastases: a literature review.Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2011 Dec;11(6):693-700. doi: 10.1586/erp.11.66. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2011. PMID: 22098285 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Brain Metastases and Associated Neurocognitive Aspects on Health Utility Scores in EGFR Mutated and ALK Rearranged NSCLC: A Real World Evidence Analysis.Oncologist. 2019 Jul;24(7):e501-e509. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0544. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30952820 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Brain Tumours upon Medical Decision-Making Capacity.Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 May 2;21(6):55. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0793-3. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31049786 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life of patients with brain metastases selected for stereotactic radiosurgery.J Neurooncol. 2019 Jul;143(3):537-546. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03186-z. Epub 2019 May 9. J Neurooncol. 2019. PMID: 31073966 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of EGFR-Directed Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (EGFR-TKI) with Radiotherapy in Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A 2010-2019 Retrospective Cohort Study.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 1;15(11):3015. doi: 10.3390/cancers15113015. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296975 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Life and Cognitive Function Evaluations and Interventions for Patients with Brain Metastases in the Radiation Oncology Clinic.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 1;14(17):4301. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174301. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schouten LJ, Rutten J, Huveneers HA, et al. Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer. 2002;94(10):2698–2705. - PubMed
-
- Kaal EC, Niel CG, Vecht CJ. Therapeutic management of brain metastasis. Lancet Neurol. 2005;4(5):289–298. - PubMed
-
- Meyers CA, Smith JA, Bezjak A, et al. Neurocognitive function and progression in patients with brain metastases treated with whole-brain radiation and motexafin gadolinium: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(1):157–165. - PubMed
-
- Chang EL, Wefel JS, Maor MH, et al. A pilot study of neurocognitive function in patients with one to three new brain metastases initially treated with stereotactic radiosurgery alone. Neurosurgery. 2007;60(2):277–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

