Drug-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 26386112
- PMCID: PMC4666974
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00554.2015
Drug-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiotoxicity
Abstract
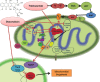
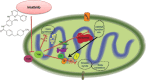
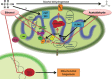
Mitochondria has an essential role in myocardial tissue homeostasis; thus deterioration in mitochondrial function eventually leads to cardiomyocyte and endothelial cell death and consequent cardiovascular dysfunction. Several chemical compounds and drugs have been known to directly or indirectly modulate cardiac mitochondrial function, which can account both for the toxicological and pharmacological properties of these substances. In many cases, toxicity problems appear only in the presence of additional cardiovascular disease conditions or develop months/years following the exposure, making the diagnosis difficult. Cardiotoxic agents affecting mitochondria include several widely used anticancer drugs [anthracyclines (Doxorubicin/Adriamycin), cisplatin, trastuzumab (Herceptin), arsenic trioxide (Trisenox), mitoxantrone (Novantrone), imatinib (Gleevec), bevacizumab (Avastin), sunitinib (Sutent), and sorafenib (Nevaxar)], antiviral compound azidothymidine (AZT, Zidovudine) and several oral antidiabetics [e.g., rosiglitazone (Avandia)]. Illicit drugs such as alcohol, cocaine, methamphetamine, ecstasy, and synthetic cannabinoids (spice, K2) may also induce mitochondria-related cardiotoxicity. Mitochondrial toxicity develops due to various mechanisms involving interference with the mitochondrial respiratory chain (e.g., uncoupling) or inhibition of the important mitochondrial enzymes (oxidative phosphorylation, Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle, mitochondrial DNA replication, ADP/ATP translocator). The final phase of mitochondrial dysfunction induces loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and an increase in mitochondrial oxidative/nitrative stress, eventually culminating into cell death. This review aims to discuss the mechanisms of mitochondrion-mediated cardiotoxicity of commonly used drugs and some potential cardioprotective strategies to prevent these toxicities.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; drug development; heart; heart failure; reactive oxygen species; toxicology.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Arcamone F, Cassinelli G, Fantini G, Grein A, Orezzi P, Pol C, Spalla C. Adriamycin, 14-hydroxydaunomycin, a new antitumor antibiotic from S. peucetius var. caesius. Biotechnol Bioeng 11: 1101–1110, 1969. - PubMed
-
- Archer SL. Mitochondrial dynamics—mitochondrial fission and fusion in human diseases. N Engl J Med 369: 2236–2251, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong GT, Joshi VM, Ness KK, Marwick TH, Zhang N, Srivastava D, Griffin BP, Grimm RA, Thomas J, Phelan D, Collier P, Krull KR, Mulrooney DA, Green DM, Hudson MM, Robison LL, Plana JC. Comprehensive Echocardiographic Detection of Treatment-Related Cardiac Dysfunction in Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer: Results From the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 65: 2511–2522, 2015. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Awtry EH, Philippides GJ. Alcoholic and cocaine-associated cardiomyopathies. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 52: 289–299, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Bai P, Mabley JG, Liaudet L, Virag L, Szabo C, Pacher P. Matrix metalloproteinase activation is an early event in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Oncol Rep 11: 505–508, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

