Combined activation of the energy and cellular-defense pathways may explain the potent anti-senescence activity of methylene blue
- PMID: 26386875
- PMCID: PMC4588422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.09.004
Combined activation of the energy and cellular-defense pathways may explain the potent anti-senescence activity of methylene blue
Abstract
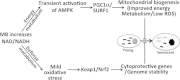
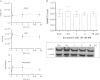
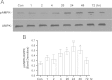
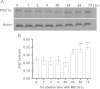
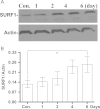
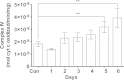
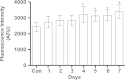
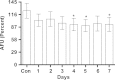
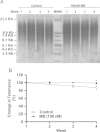
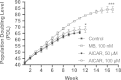
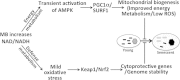
Methylene blue (MB) delays cellular senescence, induces complex-IV, and activates Keap1/Nrf2; however, the molecular link of these effects to MB is unclear. Since MB is redox-active, we investigated its effect on the NAD/NADH ratio in IMR90 cells. The transient increase in NAD/NADH observed in MB-treated cells triggered an investigation of the energy regulator AMPK. MB induced AMPK phosphorylation in a transient pattern, which was followed by the induction of PGC1α and SURF1: both are inducers of mitochondrial and complex-IV biogenesis. Subsequently MB-treated cells exhibited >100% increase in complex-IV activity and a 28% decline in cellular oxidants. The telomeres erosion rate was also significantly lower in MB-treated cells. A previous research suggested that the pattern of AMPK activation (i.e., chronic or transient) determines the AMPK effect on cell senescence. We identified that the anti-senescence activity of MB (transient activator) was 8-times higher than that of AICAR (chronic activator). Since MB lacked an effect on cell cycle, an MB-dependent change to cell cycle is unlikely to contribute to the anti-senescence activity. The current findings in conjunction with the activation of Keap1/Nrf2 suggest a synchronized activation of the energy and cellular defense pathways as a possible key factor in MB's potent anti-senescence activity.
Keywords: AMPK; Complex-IV; Mitochondria; NAD; Oxidants; Senescence; Telomeres.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Central role of nitric oxide synthase in AICAR and caffeine-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in L6 myocytes.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Mar;108(3):589-95. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00377.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 31. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20044477
-
Activation of insulin signaling and energy sensing network by AICAR, an AMPK activator in insulin resistant rat tissues.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;26(6):563-74. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2014-0122. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26124049
-
AICAR induces mitochondrial apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells through an AMPK-dependent pathway.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jan;50(1):23-30. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3775. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27878239 Free PMC article.
-
Turn up the power - pharmacological activation of mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse models.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;171(8):1818-36. doi: 10.1111/bph.12413. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24102298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual control of mitochondrial biogenesis by sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 3.Mitochondrion. 2013 Nov;13(6):755-61. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Mitochondrion. 2013. PMID: 23583953 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired Cardiac AMPK (5'-Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase) and Ca2+-Handling, and Action Potential Duration Heterogeneity in Ibrutinib-Induced Ventricular Arrhythmia Vulnerability.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Jun 18;13(12):e032357. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.032357. Epub 2024 Jun 6. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38842296 Free PMC article.
-
Antiferroptotic Activity of Phenothiazine Analogues: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Oxidative Stress Related Disease.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Sep 15;11(11):2165-2173. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00293. eCollection 2020 Nov 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 33214825 Free PMC article.
-
Methylene blue does not bypass Complex III antimycin block in mouse brain mitochondria.FEBS Lett. 2019 Mar;593(5):499-503. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13332. Epub 2019 Feb 20. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 30734287 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis as a Way for Active Longevity: Interaction Between the Nrf2 and PGC-1α Signaling Pathways.Front Genet. 2019 May 14;10:435. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00435. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31139208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Hydromethylthionine in the Line 66 Model of Frontotemporal Dementia Demonstrates Actions on Tau-Dependent and Tau-Independent Networks.Cells. 2021 Aug 22;10(8):2162. doi: 10.3390/cells10082162. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tyner S.D., Venkatachalam S., Choi J., Jones S., Ghebranious N., Igelmann H., Lu X., Soron G., Cooper B., Brayton C., Park S.H., Thompson T., Karsenty G., Bradley A., Donehower L.A. p53 mutant mice that display early ageing-associated phenotypes. Nature. 2002;415:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Geng Y.Q., Guan J.T., Xu X.H., Fu Y.C. Senescence-associated beta-galactosidase activity expression in aging hippocampal neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;396:866–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

