Novel minimally invasive laser treatment of urinary incontinence in women
- PMID: 26388213
- PMCID: PMC5396289
- DOI: 10.1002/lsm.22416
Novel minimally invasive laser treatment of urinary incontinence in women
Abstract
Background and objective: Urinary incontinence (UI) is a common disorder that affects women of various ages and impacts all aspects of life. Our aim was to evaluate the non-invasive erbium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Er:YAG) laser that exploits its thermal effect and has been used in reconstructive and rejuvenation surgery as a potential treatment strategy for stress UI (SUI) and mixed UI (MUI).
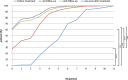
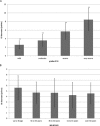
Study design/materials and methods: We included 175 women (aged 49.7 ± 10 years) with newly diagnosed SUI (66% of women) and MUI (34%), respectively. Patients were clinically examined and classified by incontinence types (SUI and MUI) and grades (mild, moderate, severe, and very severe) using International Consultation on Incontinence Modular Questionnaire (ICIQ) and assessing Incontinence Severity Index (ISI). Using Er:YAG laser, we performed on average 2.5 ± 0.5 procedures in each woman separated by a 2 month period. At each session, clinical examination was performed, ICIQ and ISI assessed and treatment discomfort measured with visual analog system (VAS) pain scale, and adverse effects and patients' satisfaction were followed. Follow-ups were performed at 2, 6, and 12 months after the treatment.
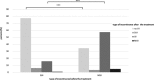
Results: After the treatment, ISI decreased for 2.6 ± 1.0 points in patients diagnosed with mild UI before the treatment, for 3.6 ± 1.4 points in those with moderate UI, for 5.7 ± 1.8 points in those with severe UI and for 8.4 ± 2.6 in those with very severe UI (P < 0.001, paired samples t-test). Altogether, in 77% patients diagnosed with SUI, a significant improvement was found after treatment, while only 34% of women with MUI exhibited no UI at one year follow-up. Age did not affect the outcome. No major adverse effects were noticed in either group.
Conclusion: The results of our study, have shown that new non-invasive Er:YAG laser could be regarded as a promising additional treatment strategy for SUI with at least one year lasting positive effects. On the other hand, it does not seem appropriate for treating MUI.
Keywords: Er-Yag laser; gynecology; mixed urinary incontinence; non-invasive procedure; stress urinary incontinence.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of Erbium: Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser Treatment in Chinese Women with Mild-to-Moderate Stress Urinary Incontinence.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2024 May;33(5):685-691. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2023.0609. Epub 2024 Apr 1. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2024. PMID: 38563974
-
Non-ablative Er:YAG laser therapy effect on stress urinary incontinence related to quality of life and sexual function: A randomized controlled trial.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018 May;224:153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.03.038. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018. PMID: 29604548 Clinical Trial.
-
Erbium:YAG laser treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: midterm data.Int Urogynecol J. 2020 Sep;31(9):1859-1866. doi: 10.1007/s00192-019-04148-9. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Int Urogynecol J. 2020. PMID: 31828400
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser Therapy for Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Lasers Surg Med. 2025 Apr;57(4):297-305. doi: 10.1002/lsm.70012. Epub 2025 Apr 6. Lasers Surg Med. 2025. PMID: 40189916
-
Vaginal Laser Therapy for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence: New Solutions for a Well-Known Issue-A Concise Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Apr 4;58(4):512. doi: 10.3390/medicina58040512. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35454351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of CO2 Vaginal Laser in the Treatment of Recurrent, Post-Coital and Interstitial Cystitis: A Multicentric Prospective Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 17;13(12):3550. doi: 10.3390/jcm13123550. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38930079 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of non-ablative ErYAG laser for mild to moderate stress urinary incontinence: a prospective, multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Apr 16;40(1):195. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04400-3. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40238038 Clinical Trial.
-
Variable heat shock response model for medical laser procedures.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Aug;34(6):1147-1158. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-02704-1. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30607720
-
Steering light in fiber-optic medical devices: a patent review.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2022 Mar;19(3):259-271. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2022.2054334. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2022. PMID: 35298323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating Vaginal Relaxation Syndrome Using Erbium: Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Fractional Laser: A Retrospective Study.Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2022 Feb 14;11(1):23-27. doi: 10.4103/GMIT.GMIT_141_20. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2022. PMID: 35310128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacLennan AH, Taylor AW, Wilson DH, Wilson D. The prevalence of pelvic floor disorders and their relationship to gender, age, parity and mode of delivery. BJOG 2000; 107(12):1460–1470. - PubMed
-
- Castro RA, Arruda RM, Bortolini MAT. Female urinary incontinence: Effective treatment strategies. Climacteric 2014; 17:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Norton P, Brubaker L. Urinary incontinence in women. Lancet 2006; 367:57–67. - PubMed
-
- Nyström E, Sjöström M, Stenlund H, Samuelsson E. ICIQ symptom and quality of life instruments measure clinically relevant improvements in women with stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 2014;DOI: 10.1002/nau.22657 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

