LDL suppresses angiogenesis through disruption of the HIF pathway via NF-κB inhibition which is reversed by the proteasome inhibitor BSc2118
- PMID: 26388611
- PMCID: PMC4745795
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4943
LDL suppresses angiogenesis through disruption of the HIF pathway via NF-κB inhibition which is reversed by the proteasome inhibitor BSc2118
Abstract
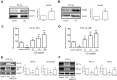
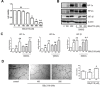
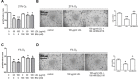
Since disturbance of angiogenesis predisposes to ischemic injuries, attempts to promote angiogenesis have been made to improve clinical outcomes of patients with many ischemic disorders. While hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) stimulate vascular remodeling and angiogenesis, hyperlipidemia impairs angiogenesis in response to various pro-angiogenic factors. However, it remains uncertain how HIFs regulate angiogenesis under hyperlipidemia. Here, we report that exposure to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) suppressed in vitro angiogenesis of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Whereas LDL exposure diminished expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α induced by hypoxia, it inhibited DMOG- and TNFα-induced HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression in normoxia. Notably, in both hypoxia and normoxia, LDL markedly reduced expression of HIF-1β, a constitutively stable HIF subunit, an event associated with NF-κB inactivation. Moreover, knockdown of HIF-1β down-regulated HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression, in association with increased HIF-1α hydroxylation and 20S proteasome activity after LDL exposure. Significantly, the proteasome inhibitor BSc2118 prevented angiogenesis attenuation by LDL through restoring expression of HIFs. Together, these findings argue that HIF-1β might act as a novel cross-link between the HIF and NF-κB pathways in suppression of angiogenesis by LDL, while proteasome inhibitors might promote angiogenesis by reactivating this signaling cascade under hyperlipidemia.
Keywords: HIF; NF-κB; angiogenesis; low-density lipoprotein; proteasome inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impairment of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis by LDL involves a HIF-centered signaling network linking inflammatory TNFα and angiogenic VEGF.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Jan 18;11(2):328-349. doi: 10.18632/aging.101726. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 30659163 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating the hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathway as a therapeutic modality to regulate retinal angiogenesis.Exp Eye Res. 2009 Nov;89(5):700-17. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.06.013. Epub 2009 Jul 4. Exp Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19580810
-
NcoA2-Dependent Inhibition of HIF-1α Activation Is Regulated via AhR.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Dec;148(2):517-30. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv199. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26350169
-
Regulation of gene expression by the hypoxia-inducible factors.Mol Interv. 2002 Jul;2(4):229-43. doi: 10.1124/mi.2.4.229. Mol Interv. 2002. PMID: 14993394 Review.
-
Adaptive and maladaptive cardiorespiratory responses to continuous and intermittent hypoxia mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors 1 and 2.Physiol Rev. 2012 Jul;92(3):967-1003. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2011. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22811423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of PD-L1 Expression by NF-κB in Cancer.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 25;11:584626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584626. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33324403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The signaling pathway of hypoxia inducible factor in regulating gut homeostasis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 27;14:1289102. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1289102. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37965556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB and Its Role in Checkpoint Control.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 31;21(11):3949. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113949. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32486375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impairment of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis by LDL involves a HIF-centered signaling network linking inflammatory TNFα and angiogenic VEGF.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Jan 18;11(2):328-349. doi: 10.18632/aging.101726. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 30659163 Free PMC article.
-
Burgeoning Exploration of the Role of Natural Killer Cells in Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 May 12;13:886931. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.886931. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sen Banerjee S, Thirunavukkarasu M, Tipu Rishi M, Sanchez JA, Maulik N, Maulik G. HIF-prolyl hydroxylases and cardiovascular diseases. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2012;22:347–358. - PubMed
-
- Rajagopalan S, Olin J, Deitcher S, Pieczek A, Laird J, Grossman PM, Goldman CK, McEllin K, Kelly R, Chronos N. Use of a constitutively active hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha transgene as a therapeutic strategy in no-option critical limb ischemia patients: phase I dose-escalation experience. Circulation. 2007;115:1234–1243. - PubMed
-
- Duan S, Shao G, Yu L, Ren C. Angiogenesis contributes to the neuroprotection induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Int J Neurosci. 2015;125:625–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

