Evaluation of Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions (DPOAEs) among workers at an Industrial Company exposed to different industrial noise levels in 2014
- PMID: 26388979
- PMCID: PMC4574699
- DOI: 10.14661/2015.1126-1134
Evaluation of Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions (DPOAEs) among workers at an Industrial Company exposed to different industrial noise levels in 2014
Abstract
Background: Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is usually one of the main problems in industrial settings. The aim of this study was to determine whether changes in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in different DPOAE are caused by exposure to different levels of noise at different time intervals among workers exposed to noise.
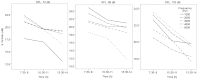
Methods: This case-control study was conducted in the autumn of 2014 on 45 workers at Gol Gohar Mining and Industrial Company, which is located in Sirjan in southeast Iran. The workers were divided into three groups based on their noise exposure, i.e., 1) 15 office workers as a control group with exposure to low levels of noise, 2) 15 workers from manufacturing departments who were exposed to a medium level of noise, and 3) 15 workers from manufacturing departments who were exposed to high levels of noise. The SNRs at the frequencies of 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 6000 Hz were measured in both ears at three different time intervals during the shift work. SNRs of 6 or greater were considered as inclusion criterion. Repeated measures, the Spearman rank-order correlation test, and paired t-test analyses were used with α = 0.05 being the level of significance.
Results: For all frequencies in the right and left ears, the SNR values were more than 6, thus all SNR values were considered as acceptable responses. The effects of time and sound pressure level (SPL) on SNR were significant for the right and left ears (p = 0.027 and < 0.001, respectively). There was a statistically significant correlation between the SNR values in the right and left ears for the time intervals 7:30-8:00 A.M. and 13:30-14:00 P.M., which implied that an increase in the duration of exposure led to reduced SNR values (p = 0.024, r = 0.948).
Conclusions: The comparison of the SNR values in the right and left ears (for all frequencies and the three different SPLs) indicated that the values decreased during the shift work.
Keywords: hearing loss; noise-induced; otoacoustic emissions; signal-to-noise ratio.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling signal-to-noise ratio of otoacoustic emissions in workers exposed to different industrial noise levels.Noise Health. 2016 Nov-Dec;18(85):391-398. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.195808. Noise Health. 2016. PMID: 27991472 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships among standard and wideband measures of middle ear function and distortion product otoacoustic emissions.J Am Acad Audiol. 2011 May;22(5):253-64. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.22.5.2. J Am Acad Audiol. 2011. PMID: 21756841 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the effects of occupational noise exposure on serum aldosterone and potassium among industrial workers.Noise Health. 2016 Jan-Feb;18(80):1-6. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.174358. Noise Health. 2016. PMID: 26780955 Free PMC article.
-
Distortion product otoacoustic emissions in an industrial setting.Noise Health. 2009 Apr-Jun;11(43):103-10. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.50695. Noise Health. 2009. PMID: 19414930
-
Identification of neonatal hearing impairment: distortion product otoacoustic emissions during the perinatal period.Ear Hear. 2000 Oct;21(5):400-24. doi: 10.1097/00003446-200010000-00007. Ear Hear. 2000. PMID: 11059701
Cited by
-
Modeling signal-to-noise ratio of otoacoustic emissions in workers exposed to different industrial noise levels.Noise Health. 2016 Nov-Dec;18(85):391-398. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.195808. Noise Health. 2016. PMID: 27991472 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Occupational Noise Exposure on Serum Cortisol Concentration of Night-shift Industrial Workers: A Field Study.Saf Health Work. 2019 Mar;10(1):109-113. doi: 10.1016/j.shaw.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Saf Health Work. 2019. PMID: 30949389 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the effects of various sound pressure levels on the level of serum aldosterone concentration in rats.Noise Health. 2017 Jul-Aug;19(89):200-206. doi: 10.4103/nah.NAH_64_16. Noise Health. 2017. PMID: 28816207 Free PMC article.
-
Does occupational noise matter amongst manufacturing (small and medium enterprises) workers? Empirical evidence from Magaba, Mbare, Zimbabwe.S Afr J Commun Disord. 2020 Mar 3;67(2):e1-e11. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v67i2.680. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2020. PMID: 32129661 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Mutation of m.3243A>G together with m.16093T>C Associated with Atypical Clinical Features in a Pedigree with MIDD Syndrome.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Apr 4;2019:5184647. doi: 10.1155/2019/5184647. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31143779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halvani GH, Zare M, Barkhordari A. Noise induced hearing loss among textile workers of Taban factories in Yazd. Journal of Birjand University of Medical Sciences. 2009;15(4):69–74. (In Persian)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources