Trends in relative survival in patients with a diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in Ontario: a population-based retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 26389099
- PMCID: PMC4565177
- DOI: 10.9778/cmajo.20140118
Trends in relative survival in patients with a diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in Ontario: a population-based retrospective cohort study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Trends in relative survival in patients with a diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in Ontario: a population-based retrospective cohort study.CMAJ Open. 2015 Oct 15;3(4):E359. doi: 10.9778/cmajo.20150109. eCollection 2015 Oct-Dec. CMAJ Open. 2015. PMID: 27022599 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing and survival rates are poor. Our objectives were to estimate the relative survival over time in patients with HCC in Ontario and to examine potential factors associated with excess mortality risk.
Methods: We performed a population-based retrospective cohort analysis involving patients with a diagnosis of HCC in Ontario between 1990 and 2009 using data extracted from the Ontario Cancer Registry. Relative survival was estimated by controlling for background mortality using expected mortality from Ontario life tables. A generalized linear model was used to estimate the excess mortality risk for important factors.
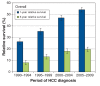
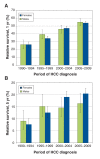
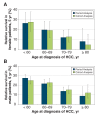
Results: A total of 5645 patients had HCC diagnosed during the study period; 4412 (78.2%) of these patients were male. Improvements in 1-year relative survival were observed across all age groups over time: the highest was among those patients less than 60 years of age who had a diagnosis of HCC during 2005-2009, with 1-year survival exceeding 50% for both sexes. However, the overall 5-year relative survival did not exceed 28%. The excess mortality risk decreased with increased years of follow-up, recent diagnosis, and curative or noncurative treatments for HCC, whereas excess mortality risk increased with age.
Interpretation: Although improving, the prognosis for HCC remains poor. Our findings highlight the importance of effective prevention and treatment for HCC to reduce the burden of disease and improve health care systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010;127:2893-917. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007;132:2557-76. - PubMed
-
- Pocobelli G, Cook LS, Brant R, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence trends in Canada: analysis by birth cohort and period of diagnosis. Liver Int 2008;28:1272-9. - PubMed
-
- Dyer Z, Peltekian K, van Zanten SV. Review article: the changing epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Canada. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;22:17-22. - PubMed
-
- Canadian Cancer Society’s Advisory Committee on Cancer Statistics. Canadian cancer statistics 2013 Toronto: Canadian Cancer Society; 2013. Available: www.cancer.ca/~/media/cancer.ca/CW/cancer%20information/cancer%20101/Can... (accessed 2015 May 4).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
