Translocation-coupled DNA cleavage by the Type ISP restriction-modification enzymes
- PMID: 26389736
- PMCID: PMC4636054
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1926
Translocation-coupled DNA cleavage by the Type ISP restriction-modification enzymes
Abstract
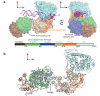
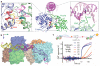
Production of endonucleolytic double-strand DNA breaks requires separate strand cleavage events. Although catalytic mechanisms for simple, dimeric endonucleases are known, there are many complex nuclease machines that are poorly understood. Here we studied the single polypeptide Type ISP restriction-modification (RM) enzymes, which cleave random DNA between distant target sites when two enzymes collide after convergent ATP-driven translocation. We report the 2.7-Å resolution X-ray crystal structure of a Type ISP enzyme-DNA complex, revealing that both the helicase-like ATPase and nuclease are located upstream of the direction of translocation, an observation inconsistent with simple nuclease-domain dimerization. Using single-molecule and biochemical techniques, we demonstrate that each ATPase remodels its DNA-protein complex and translocates along DNA without looping it, leading to a collision complex in which the nuclease domains are distal. Sequencing of the products of single cleavage events suggests a previously undescribed endonuclease model, where multiple, stochastic strand-nicking events combine to produce DNA scission.
Figures




References
Reference list
Methods-only references
-
- LeMaster DM, Richards FM. NMR sequential assignment of Escherichia coli thioredoxin utilizing random fractional deuteriation. Biochemistry. 1988;27:142–150. - PubMed
-
- French S, Wilson K. On the treatment of negative intensity observations. Acta Crystallogr. A. 1978;34:517–525.
-
- Cowtan KD, Zhang KYJ. Density modification for macromolecular phase improvement. Prog. Biophy. Mol. Biol. 1999;72:245–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

